Clinical trials for cytoprotection in stroke
- PMID: 15717007
- PMCID: PMC534912
- DOI: 10.1602/neurorx.1.1.46
Clinical trials for cytoprotection in stroke
Abstract
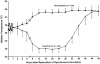
To date, many cytoprotective drugs have reached the stage of pivotal phase 3 efficacy trials in acute stroke patients. (Table 1) Unfortunately, throughout the neuroprotective literature, the phrase "failure to demonstrate efficacy" prevails as a common thread among the many neutral or negative trials, despite the largely encouraging results encountered in preclinical studies. The reasons for this discrepancy are multiple, and have been discussed by Dr. Zivin in his review. Many of the recent trials have addressed deficiencies of the previous ones with more rigorous trial design, including more specific patient selection criteria (ensure homogeneity of stroke location and severity), stratified randomization algorithms (time-to-treat), narrowed therapeutic time-window and pharmacokinetic monitoring. Current trials have also incorporated biologic surrogate markers of toxicity and outcome such as drug levels and neuroimaging. Lastly, multi-modal therapies and coupled cytoprotection/reperfusion strategies are being investigated to optimize tissue salvage. This review will focus on individual therapeutic strategies and we will emphasize what we have learned from these trials both in terms of trial design and the biologic effect (or lack thereof) of these agents.
Figures


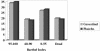
References
-
- Grotta JC. Clinical aspects of the use of calcium antagonists in cerebrovascular disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 14: 373–390, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Petruk KC, West M, Mohr G, Weir BK, Benoit BG, Gentili F et al. Nimodipine treatment in poor-grade aneurysm patients: results of a multicenter double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J Neurosurg 68: 505–517, 1988. - PubMed
-
- Ohman J, Servo A, Heiskanen O. Long-term effects of nimodipine on cerebral infarcts and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and surgery. J Neurosurg 74: 8–13, 1991 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

