Quantitative magnetic resonance techniques as surrogate markers of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 15717020
- PMCID: PMC534925
- DOI: 10.1602/neurorx.1.2.196
Quantitative magnetic resonance techniques as surrogate markers of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Recent advances in understanding the molecular biology of Alzheimer's disease (AD) offer the promise of useful therapeutic intervention in the foreseeable future. Hence, improved methods for early diagnosis and noninvasive surrogates of disease severity in AD have become more imperative. Various quantitative magnetic resonance (MR) techniques that measure the anatomic, biochemical, microstructural, functional, and blood-flow changes are being evaluated as possible surrogate measures of disease progression. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies indicate that MR-based volume measurements are potential surrogates of disease progression in AD, starting from the preclinical stages. The validity of MR-based volumetry as a surrogate marker for therapeutic efficacy in AD remains to be tested in a positive disease-modifying drug trial. Recent development of amyloid imaging tracers for positron emission tomography has been a major breakthrough in the field of imaging markers for AD. Efforts to image plaques are also underway in MR imaging. As with indirect MR measures, these approaches of directly imaging the pathological substrate will need to undergo a validation process with longitudinal studies to prove their usefulness as surrogate markers in AD.
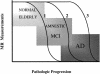
Figures

Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance markers for early diagnosis and progression of Alzheimer's disease.Expert Rev Neurother. 2005 Sep;5(5):663-70. doi: 10.1586/14737175.5.5.663. Expert Rev Neurother. 2005. PMID: 16162090 Review.
-
In vivo detection of microstructural correlates of brain pathology in preclinical and early Alzheimer Disease with magnetic resonance imaging.Neuroimage. 2017 Mar 1;148:296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.026. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27989773 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging in Alzheimer disease: an evidence-based review.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2003 May;13(2):197-209. doi: 10.1016/s1052-5149(03)00025-x. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2003. PMID: 13677801 Review.
-
Applications of neuroimaging to disease-modification trials in Alzheimer's disease.Behav Neurol. 2009;21(1):129-36. doi: 10.3233/BEN-2009-0241. Behav Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19847051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of Alzheimer's pathology in the brains of living transgenic mice: a new tool in Alzheimer's disease research.Neuroscientist. 2007 Feb;13(1):38-48. doi: 10.1177/1073858406295610. Neuroscientist. 2007. PMID: 17229974 Review.
Cited by
-
Saturation Transfer MRI for Detection of Metabolic and Microstructural Impairments Underlying Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's Disease.Brain Sci. 2021 Dec 30;12(1):53. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12010053. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 35053797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The validity of biomarkers as surrogate endpoints in Alzheimer's disease by means of the Quantitative Surrogate Validation Level of Evidence Scheme (QSVLES).J Nutr Health Aging. 2009 Apr;13(4):376-87. doi: 10.1007/s12603-009-0049-2. J Nutr Health Aging. 2009. PMID: 19300886 Review.
-
Network Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's Disease via MRI Based Shape Diffeomorphometry and High-Field Atlasing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 May 15;3:54. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00054. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26284236 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal pattern of regional brain volume change differentiates normal aging from MCI.Neurology. 2009 Jun 2;72(22):1906-13. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a82634. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19487648 Free PMC article.
-
Using deep Siamese neural networks for detection of brain asymmetries associated with Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment.Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Dec;64:190-199. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31319126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shoghi-Jadid K, Small GW, Agdeppa ED et al. Localization of neurofibrillary tangles and β-amyloid plaques in the brains of living patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 10: 24–34, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 82: 239–259, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Seab JB, Jagust WJ, Wong STS et al. Quantitive NMR measurements of hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Magn Reson Med 8: 200–208, 1988. - PubMed
-
- Kesslak JP, Nalcioglu O, Cotman CW. Quantification of magnetic resonance scans for hippocampal and parahippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 41: 51–54, 1991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

