Molecular neuroimaging in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 15717021
- PMCID: PMC534926
- DOI: 10.1602/neurorx.1.2.206
Molecular neuroimaging in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
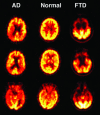
Considerable data exist to support the use of positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanning as biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease (AD). The techniques are reasonably sensitive and specific in differentiating AD from normal aging, and recent studies with pathological confirmation show good sensitivity and specificity in differentiating AD from other dementias. These techniques also can detect abnormalities in groups of asymptomatic and presymptomatic individuals and may be able to predict decline to dementia. However, there are a number of existing questions related to the use of these techniques in samples that are fully representative of the spectrum of patients with dementia. For example, it is unclear how well PET and SPECT perform in comparison to a clinical diagnosis obtained in the same patient group, when autopsy is used as a gold standard. It will also be important to know what PET and SPECT add to the certainty of diagnosis in addition to the standard clinical diagnosis. Despite these unanswered questions, PET and SPECT may have application as biomarkers for AD in a number of clinical and research settings, especially in academic centers, where most of the existing studies have been done.
Figures
References
-
- Kety SS. Human cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption as related to aging. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis 35: 31–45, 1956. - PubMed
-
- Frackowiak RSJ, Pozzili C, Legg NJ, Du Boulay GH, Marshall J, Lenzi L et al. Regional cerebral oxygen supply and utilization in dementia: a clinical and physiological study with oxygen-15 and positron tomography. Brain 104: 753–778, 1981. - PubMed
-
- Friedland RP, Budinger TF, Ganz E, Yano Y, Mathis CA, Koss B et al. Regional cerebral metabolic alterations in dementia of the Alzheimer type: positron emission tomography with [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 590–598, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Benson DF, Kuhl DE, Hawkins RA, Phelps ME, Cummings JL, Tsai SY. The fluorodeoxyglucose 18F scan in Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia. Arch Neurol 40: 711–714, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Johnson KA, Mueller ST, Walshe TM, English RJ, Holman BL. Cerebral perfusion imaging in Alzheimer’s disease: use of single photon emission computed tomography and iofetamine hydrochloride I 123. Arch Neurol 44: 165–168, 1987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

