Huntington's disease genetics
- PMID: 15717026
- PMCID: PMC534940
- DOI: 10.1602/neurorx.1.2.255
Huntington's disease genetics
Abstract
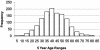
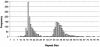
Huntington's disease (HD) is a dominantly transmitted neurodegenerative disorder with wide variation in onset age but with an average age at onset of 40 years. Children of HD gene carriers have a 50% chance of inheriting the disease. The characteristic symptoms of HD are involuntary choreiform movements, cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and behavioral changes which are chronic and progressive over the course of the illness. HD is a "trinucleotide repeat" disorder, which is caused by an increase in the number of CAG repeats in the HD gene. Repeats of 40 or larger are associated with disease expression, whereas repeats of 26 and smaller are normal. Intermediate numbers of repeats, between 27 and 35, are not associated with disease expression but may expand in paternal transmission, resulting in the disease in descendents. Repeats of 36-39 are associated with reduced penetrance whereby some develop HD and others do not. The identification of the genetic defect in HD permits direct genetic testing for the presence of the gene alteration responsible for the disease. Tests may be performed in three circumstances: (1) confirmation of diagnosis, (2) predictive testing of persons at genetic risk for inheriting HD, and (3) prenatal testing. Testing is widely available and much experience has been gained with protocols that assist the individual in making an informed choice about test options, and minimize the occurrence of adverse emotional outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Myers RH, Marans K, MacDonald ME. Huntington’s disease. In: Genetic instabilities and hereditary neurological diseases (Warren ST, Wells RT, eds), pp 301–323. New York: Academic Press, 1998.
-
- Gusella JF, Wexler NS, Conneally PM, Naylor SL, Anderson MA, Tanzi RE et al. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington’s disease. Nature 306: 234–238, 1983. - PubMed
-
- The Huntington’s Disease Research Collaborative Group. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. Cell 72: 971–983, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Duyao MP, Ambrose CM, Myers RH, Novelletto A, Persichetti F, Frontali M et al. Trinucleotide repeat length: instability and age of onset in Huntington’s disease. Nat Genet 4: 387–392, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Chong SS, Almqvist E, Telenius H, LaTray L, Nichol K, Bourdelat-Parks B et al. Contribution of DNA sequence and CAG size to mutation frequencies of intermediate alleles for Huntington disease: evidence from single sperm analyses. Hum Mol Genet 6: 301–309, 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

