Active efflux across the blood-brain barrier: role of the solute carrier family
- PMID: 15717059
- PMCID: PMC539323
- DOI: 10.1602/neurorx.2.1.73
Active efflux across the blood-brain barrier: role of the solute carrier family
Abstract
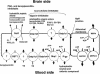
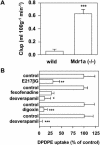
The brain uptake of xenobiotics is restricted by the blood-brain brain barrier formed by brain capillary endothelial cells. Active efflux transport systems in the blood-brain barrier work as a detoxification system in the brain by facilitating removal of xenobiotic compounds from the brain. Drugs, acting in the brain, have to overcome such efflux mechanisms to achieve clinically significant concentration in the brain. Multiple transporters are involved in this efflux transport in the brain capillaries. In the past few years, considerable progress has been made in the cloning of these transporters and their functional characterization after heterologous expression. Members of the solute carrier family (SLC) play an important role in the efflux transport, especially for organic anions, which include organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP/SLCO) and organic anion transporters (OAT/SLC22A). It is believed that coordination of the members of SLC family, and ABC transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance protein, and breast cancer-resistant protein (BCRP/ABCG2), allows an efficient vectorial transport across the endothelial cells to remove xenobiotics from the brain. In this review, we shall summarize our current knowledge about their localization, molecular and functional characteristics, and substrate and inhibitor specificity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Membrane transporter proteins: a challenge for CNS drug development.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006;8(3):311-21. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2006.8.3/fgirardin. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17117613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitubercular Agent Delamanid and Metabolites as Substrates and Inhibitors of ABC and Solute Carrier Transporters.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 May 23;60(6):3497-508. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03049-15. Print 2016 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27021329 Free PMC article.
-
Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 May;76(1):22-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.04.006. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16011870 Review.
-
Solute Carriers in the Blood-Brain Barier: Safety in Abundance.Neurochem Res. 2017 Mar;42(3):795-809. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2030-x. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27503090 Review.
-
Ontogeny of ABC and SLC transporters in the microvessels of developing rat brain.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;30(2):107-16. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12175. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26662930
Cited by
-
Low Molecular Weight (poly)Phenol Metabolites Across the Blood-Brain Barrier: The Underexplored Journey.Brain Plast. 2021 Feb 9;6(2):193-214. doi: 10.3233/BPL-200099. Brain Plast. 2021. PMID: 33782650 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo investigation of dexibuprofen derivatives for CNS delivery.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Feb;33(2):279-88. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.144. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22301864 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of common cerebral small vessel disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Feb;18(2):84-101. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00592-8. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34987231 Review.
-
The transport of anti-HIV drugs across blood-CNS interfaces: summary of current knowledge and recommendations for further research.Antiviral Res. 2009 May;82(2):A99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.12.013. Epub 2009 Jan 25. Antiviral Res. 2009. PMID: 19176219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting blood-brain barrier changes during inflammatory pain: an opportunity for optimizing CNS drug delivery.Ther Deliv. 2011 Aug;2(8):1015-41. doi: 10.4155/tde.11.67. Ther Deliv. 2011. PMID: 22468221 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pardridge WM. Introduction to the blood-brain barrier. Cambridge University Press, 1998.
-
- Begley DJ, Brightman MW. Structural and functional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. Prog Drug Res 61: 39–78, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G, Dejana E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol Rev 84: 869–901, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

