K+ secretion activated by luminal P2Y2 and P2Y4 receptors in mouse colon
- PMID: 15718265
- PMCID: PMC1456044
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.080002
K+ secretion activated by luminal P2Y2 and P2Y4 receptors in mouse colon
Abstract
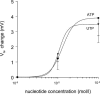
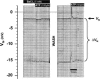
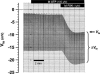
Extracellular nucleotides are important regulators of epithelial ion transport, frequently exerting their action from the luminal side. Luminal P2Y receptors have previously been identified in rat distal colonic mucosa. Their activation by UTP and ATP stimulates K+ secretion. The aim of this study was to clarify which of the P2Y receptor subtypes are responsible for the stimulated K+ secretion. To this end P2Y2 and P2Y4 knock-out mice were used to measure distal colonic ion transport in an Ussing chamber. In mouse (NMRI) distal colonic mucosa, luminal UTP and ATP with similar potency induced a rapid and transient increase of the transepithelial voltage (V(te)) (UTP: from -0.81 +/- 0.23 to 3.11 +/- 0.61 mV, n = 24), an increase of equivalent short circuit current (I(sc)) by 166.9 +/- 22.8 microA cm(-2) and a decrease of transepithelial resistance (R(te)) from 29.4 +/- 2.4 to 23.5 +/- 2.0 Omega cm2. This effect was completely inhibited by luminal Ba2+ (5 mm, n = 5) and iberiotoxin (240 nm, n = 6), indicating UTP/ATP-stimulated K+ secretion. RT-PCR analysis of isolated colonic crypts revealed P2Y2, P2Y4 and P2Y6 specific transcripts. The luminal UTP-stimulated K+ secretion was still present in P2Y2 receptor knock-out mice, but significantly reduced (DeltaV(te): 0.83 +/- 0.26 mV) compared to wild-type littermates (DeltaV(te): 2.08 +/- 0.52 mV, n = 9). In P2Y4 receptor knock-out mice the UTP-induced K+ secretion was similarly reduced. Luminal UTP-stimulated K+ secretion was completely absent in P2Y2/P2Y4 double receptor KO mice. Basolateral UTP showed no effect. In summary, these results indicate that both the P2Y2 and P2Y4 receptors are present in the luminal membrane of mouse distal colonic mucosa, and stimulation of these receptors leads to K+ secretion.
Figures


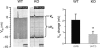
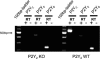


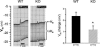
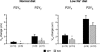

Similar articles
-
Distal colonic Na(+) absorption inhibited by luminal P2Y(2) receptors.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Sep;454(6):977-87. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0248-9. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17356885
-
Luminal ATP induces K+ secretion via a P2Y2 receptor in rat distal colonic mucosa.Pflugers Arch. 1998 Oct;436(5):712-6. doi: 10.1007/s004240050693. Pflugers Arch. 1998. PMID: 9716704
-
Mechanically evoked reflex electrogenic chloride secretion in rat distal colon is triggered by endogenous nucleotides acting at P2Y1, P2Y2, and P2Y4 receptors.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Jan 26;469(1):16-36. doi: 10.1002/cne.10961. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14689471
-
Control of epithelial transport via luminal P2 receptors.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Mar;284(3):F419-32. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00075.2002. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12556361 Review.
-
Molecular pharmacology of P2Y-receptors.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000 Nov;362(4-5):310-23. doi: 10.1007/s002100000310. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11111826 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of P2Y2 receptors in bovine cumulus oocyte complexes: effects on intracellular calcium, zona hardening and developmental competence.Purinergic Signal. 2020 Mar;16(1):85-96. doi: 10.1007/s11302-020-09690-6. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Purinergic Signal. 2020. PMID: 32043211 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy.Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):281-341. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.3. Pharmacol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16968944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Colonic potassium handling.Pflugers Arch. 2010 Apr;459(5):645-56. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0781-9. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20143237 Review.
-
P2Y2 receptor knock-out mice display normal NaCl absorption in medullary thick ascending limb.Front Physiol. 2013 Oct 9;4:280. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00280. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24130530 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 receptor transcription is increased by NF-kappa B and stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression and PGE2 released by intestinal epithelial cells.J Immunol. 2009 Oct 1;183(7):4521-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803977. Epub 2009 Sep 4. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19734210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Miras-Portugal MT, King BF, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA, Burnstock G. Characterization of the UDP-glucose receptor (re-named here the P2Y14 receptor) adds diversity to the P2Y receptor family. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:52–55. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brinson AE, Harden TK. Differential regulation of the uridine nucleotide-activated P2Y4 and P2Y6 receptors. SER-333 and SER-334 in the carboxyl terminus are involved in agonist-dependent phosphorylation desensitization and internalization of the P2Y4 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:11939–11948. - PubMed
-
- Clarke LL, Chinet TC, Boucher RC. Extracellular ATP stimulates K+ secretion across human airway epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:L1084–L1091. - PubMed
-
- Clarke LL, Harline MC, Gawenis LR, Walker NM, Turner JT, Weisman GA. Extracellular UTP stimulates electrogenic bicarbonate secretion across CFTR knockout gallbladder epithelium. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G132–G138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

