Betamethasone effects on fetal sheep cerebral blood flow are not dependent on maturation of cerebrovascular system and pituitary-adrenal axis
- PMID: 15718268
- PMCID: PMC1464428
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.077537
Betamethasone effects on fetal sheep cerebral blood flow are not dependent on maturation of cerebrovascular system and pituitary-adrenal axis
Abstract
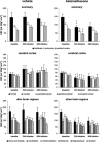
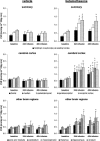
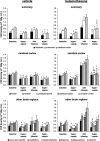
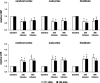
Synthetic glucocorticoids are administered to pregnant women in premature labour to accelerate fetal lung maturation at a time when fetal cerebrovascular and endocrine systems are maturing. Exposure to glucocorticoids at 0.8-0.9 of gestation increases peripheral and cerebrovascular resistance (CVR) in fetal sheep. We examined whether the increase of CVR and its adverse effect on cerebral blood flow (CBF) depend on the current level of maturation of the pituitary-adrenal axis and the cerebrovascular system. Using fluorescent microspheres, regional CBF was measured in 11 brain regions before and 24 h and 48 h after the start of 3.3 microg kg(-1) h(-1) betamethasone (n = 8) or vehicle (n = 7) infusions to fetal sheep at 0.73 of gestation. Hypercapnic challenges were performed before and 24 h after the onset of betamethasone exposure to examine betamethasone effects on cerebrovascular reactivity. Betamethasone exposure decreased CBF by approximately 40% in all brain regions after 24 h of infusion (P < 0.05). The decline in CBF was mediated by a CVR increase of 111 +/- 16% in the cerebral cortex and 129 +/- 29% in subcortical regions (P < 0.05). Hypercapnic cerebral vasodilatation and associated increase in CBF were blunted (P < 0.05). Fetal CBF recovered after 48 h of betamethasone administration. There were no differences in glucocorticoid induced CBF and CVR changes compared with our previous findings at 0.87 of gestation. We conclude that the cerebrovascular effects of antenatal glucocorticoids are independent of cerebrovascular maturation and preparturient increase in activity of the fetal pituitary-adrenal axis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of betamethasone administration to the fetal sheep in late gestation on fetal cerebral blood flow.J Physiol. 2000 Nov 1;528(Pt 3):619-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00619.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11060135 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of repeated maternal betamethasone administration on growth and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function of the ovine fetus at term.J Endocrinol. 2000 Apr;165(1):79-91. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1650079. J Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10750038
-
Effects of antenatal glucocorticoids on cerebral substrate metabolism in the preterm ovine fetus.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jan;198(1):105.e1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.007. Epub 2007 Sep 18. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008. PMID: 17880903
-
Glucocorticoid Maturation of Fetal Cardiovascular Function.Trends Mol Med. 2020 Feb;26(2):170-184. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.09.005. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Trends Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31718939 Review.
-
Cerebral blood flow self-regulation in depression.J Affect Disord. 2022 Apr 1;302:324-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.01.057. Epub 2022 Jan 13. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35032508 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis and prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage.Clin Perinatol. 2014 Mar;41(1):47-67. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Clin Perinatol. 2014. PMID: 24524446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-blind, non-inferiority, randomized controlled trial of dexamethasone 4, 5 and 6 mg for preventing adverse neonatal and maternal outcomes in very preterm to late preterm pregnancies between 29 0 and 36 6 weeks of gestation: study protocol.Reprod Health. 2025 Mar 3;22(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12978-025-01965-8. Reprod Health. 2025. PMID: 40025486 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal glucocorticoid exposure is associated with preadolescent brain development.Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Nov 1;74(9):647-55. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.03.009. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23611262 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and long-term neonatal outcomes according to differential exposure to antenatal corticosteroid therapy in preterm births prior to 24 weeks of gestation.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 4;13(6):e0198471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198471. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29864169 Free PMC article.
-
Antenatal steroids and the IUGR fetus: are exposure and physiological effects on the lung and cardiovascular system the same as in normally grown fetuses?J Pregnancy. 2012;2012:839656. doi: 10.1155/2012/839656. Epub 2012 Nov 22. J Pregnancy. 2012. PMID: 23227338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antonow-Schlorke I, Kühn B, Müller T, Schubert H, Sliwka U, Nathanielsz PW, Schwab M. Antenatal betamethasone treatment reduces synaptophysin in presynaptic terminals in the fetal sheep brain. Neurosci Lett. 2001;297:147–150. 10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01605-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antonow-Schlorke I, Müller T, Schubert H, Wicher C, Schwab M. Betamethasone related acute alterations of brain microtubule associated proteins in the fetal sheep brain are independent of baseline plasma cortisol level. Cesk Gynecol. 2002;67(Suppl. 3):3.
-
- Anwar MA, Schwab M, Poston L, Nathanielsz PW. Betamethasone-mediated vascular dysfunction and changes in hematological profile in the ovine fetus. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:H1137–H1143. - PubMed
-
- Bennet L, Kozuma S, McGarrigle HH, Hanson MA. Temporal changes in fetal cardiovascular, behavioural, metabolic and endocrine responses to maternally administered dexamethasone in the late gestation fetal sheep. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:331–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

