Cell death of bioenergetically compromised and transcriptionally challenged CLL lymphocytes by chlorinated ATP
- PMID: 15718423
- PMCID: PMC1895042
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-05-1699
Cell death of bioenergetically compromised and transcriptionally challenged CLL lymphocytes by chlorinated ATP
Abstract
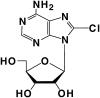
Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1) acts as a key survival factor for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. In addition, dissipation of cellular bioenergy may impose a lethal effect on these quiescent cells. Previously, in multiple myeloma cell lines we demonstrated that halogenated adenosine (8-Cl-Ado) was phosphorylated to triphosphate (8-Cl-adenosine triphosphate [ATP]), which preferentially incorporated into mRNA and inhibited RNA synthesis by premature transcription termination. Furthermore, 8-Cl-ATP accumulation was associated with a decline in cellular bioenergy. Based on these actions, we hypothesized that 8-Cl-Ado would be ideal to target CLL lymphocytes. In the present study we demonstrate that leukemic lymphocytes incubated with 8-Cl-Ado display time- and dose-dependent increase in the accumulation of 8-Cl-ATP, with a parallel depletion of the endogenous ATP pool. Inhibition of global RNA synthesis resulted in a significant decline in the expression of transcripts with a short half-life such as MCL1. Consistent to this, protein expression of MCL-1 but not B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) was decreased. Furthermore, 8-Cl-ATP induced programmed cell death, as suggested by caspases activation, cleavage of caspase 3, and PARP (poly-adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose polymerase), and increased DNA fragmentation. In conclusion, 8-Cl-Ado induces apoptosis in CLL lymphocytes by targeting cellular bioenergy as well as RNA transcription and translation of key survival genes such as MCL1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcription inhibition by flavopiridol: mechanism of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell death.Blood. 2005 Oct 1;106(7):2513-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1678. Epub 2005 Jun 21. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15972445 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of cell death of chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes by RNA-directed agent, 8-NH2-adenosine.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Sep 15;11(18):6745-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0553. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16166456
-
The natural product honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells.Blood. 2005 Jul 15;106(2):690-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-11-4273. Epub 2005 Mar 31. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15802533
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) upregulates the expression of bcl-2 in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell lines resulting in delaying apoptosis.Leukemia. 1997 Feb;11(2):258-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400556. Leukemia. 1997. PMID: 9009090
-
8-chloro-cAMP and 8-chloro-adenosine act by the same mechanism in multiple myeloma cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 15;61(14):5474-9. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11454694
Cited by
-
Transcription inhibition by flavopiridol: mechanism of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell death.Blood. 2005 Oct 1;106(7):2513-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1678. Epub 2005 Jun 21. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15972445 Free PMC article.
-
ATP analog enhances the actions of a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor in multiple myeloma cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Nov;339(2):545-54. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.184903. Epub 2011 Aug 5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21821695 Free PMC article.
-
E2F1-mediated DNA damage is implicated in 8-Cl-adenosine-induced chromosome missegregation and apoptosis in human lung cancer H1299 cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Dec;384(1-2):187-96. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1797-1. Epub 2013 Sep 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24037421
-
Polyadenylation inhibition by the triphosphates of deoxyadenosine analogues.Leuk Res. 2008 Oct;32(10):1573-81. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2008.03.010. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Leuk Res. 2008. PMID: 18433867 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of bone marrow stromal microenvironment on forodesine-induced responses in CLL primary cells.Blood. 2010 Aug 19;116(7):1083-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-246199. Epub 2010 May 4. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20442367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keating MJ. Management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a changing field. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2002;6: 350-365. - PubMed
-
- Keating MJ, O'Brien S, Lerner S, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving fludarabine regimens as initial therapy. Blood. 1998;92: 1165-1171. - PubMed
-
- Flinn IW, Byrd JC, Morrison C, et al. Fludarabine and cyclophosphamide with filgrastim support in patients with previously untreated indolent lymphoid malignancies. Blood. 2000;96: 71-75. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SM, Kantarjian HM, Cortes J, et al. Results of the fludarabine and cyclophosphamide combination regimen in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19: 1414-1420. - PubMed
-
- Boogaerts MA, Van Hoof A, Catovsky D, et al. Activity of oral fludarabine phosphate in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19: 4252-4258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

