Cell death of bioenergetically compromised and transcriptionally challenged CLL lymphocytes by chlorinated ATP
- PMID: 15718423
- PMCID: PMC1895042
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-05-1699
Cell death of bioenergetically compromised and transcriptionally challenged CLL lymphocytes by chlorinated ATP
Abstract
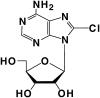
Myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1) acts as a key survival factor for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. In addition, dissipation of cellular bioenergy may impose a lethal effect on these quiescent cells. Previously, in multiple myeloma cell lines we demonstrated that halogenated adenosine (8-Cl-Ado) was phosphorylated to triphosphate (8-Cl-adenosine triphosphate [ATP]), which preferentially incorporated into mRNA and inhibited RNA synthesis by premature transcription termination. Furthermore, 8-Cl-ATP accumulation was associated with a decline in cellular bioenergy. Based on these actions, we hypothesized that 8-Cl-Ado would be ideal to target CLL lymphocytes. In the present study we demonstrate that leukemic lymphocytes incubated with 8-Cl-Ado display time- and dose-dependent increase in the accumulation of 8-Cl-ATP, with a parallel depletion of the endogenous ATP pool. Inhibition of global RNA synthesis resulted in a significant decline in the expression of transcripts with a short half-life such as MCL1. Consistent to this, protein expression of MCL-1 but not B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) was decreased. Furthermore, 8-Cl-ATP induced programmed cell death, as suggested by caspases activation, cleavage of caspase 3, and PARP (poly-adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose polymerase), and increased DNA fragmentation. In conclusion, 8-Cl-Ado induces apoptosis in CLL lymphocytes by targeting cellular bioenergy as well as RNA transcription and translation of key survival genes such as MCL1.
Figures


References
-
- Keating MJ. Management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a changing field. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2002;6: 350-365. - PubMed
-
- Keating MJ, O'Brien S, Lerner S, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving fludarabine regimens as initial therapy. Blood. 1998;92: 1165-1171. - PubMed
-
- Flinn IW, Byrd JC, Morrison C, et al. Fludarabine and cyclophosphamide with filgrastim support in patients with previously untreated indolent lymphoid malignancies. Blood. 2000;96: 71-75. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SM, Kantarjian HM, Cortes J, et al. Results of the fludarabine and cyclophosphamide combination regimen in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19: 1414-1420. - PubMed
-
- Boogaerts MA, Van Hoof A, Catovsky D, et al. Activity of oral fludarabine phosphate in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19: 4252-4258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

