A receptor domain controls the intracellular sorting of the ferrichrome transporter, ARN1
- PMID: 15719020
- PMCID: PMC554128
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600579
A receptor domain controls the intracellular sorting of the ferrichrome transporter, ARN1
Abstract
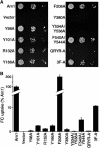
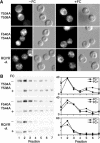
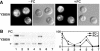
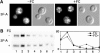
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae transporter Arn1p takes up the ferric-siderophore ferrichrome, and extracellular ferrichrome dramatically influences the intracellular trafficking of Arn1p. In the absence of ferrichrome, Arn1p sorts directly to the endosomal compartment. At low concentrations of ferrichrome, Arn1p stably relocalizes to the plasma membrane, yet little to no uptake of ferrichrome occurs at these low concentrations. At higher concentrations of ferrichrome, Arn1p cycles between the plasma membrane and endosome. Arn1p contains two binding sites for ferrichrome: one site has an affinity similar to the K(T) for transport, but the second site has a much higher affinity. Here we report that this high-affinity binding site lies within a unique extracytosolic, carboxyl-terminal domain. Mutations within this domain lead to loss of ferrichrome binding and uptake activities and missorting of Arn1p, including a failure to relocalize to the plasma membrane in the presence of ferrichrome. Mutation of phenylalanine residues in the cytosolic tail of Arn1p also lead to missorting, but without defects in ferrichrome binding. We propose that the carboxyl terminus of Arn1p contains a receptor domain that controls the intracellular trafficking of the transporter.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ferrichrome induces endosome to plasma membrane cycling of the ferrichrome transporter, Arn1p, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J. 2002 Jul 15;21(14):3632-42. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf382. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12110576 Free PMC article.
-
GGA2- and ubiquitin-dependent trafficking of Arn1, the ferrichrome transporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 May;18(5):1790-802. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-09-0861. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17344478 Free PMC article.
-
Gga2 mediates sequential ubiquitin-independent and ubiquitin-dependent steps in the trafficking of ARN1 from the trans-Golgi network to the vacuole.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 28;284(35):23830-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.030015. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19574226 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylserine is involved in the ferrichrome-induced plasma membrane trafficking of Arn1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 10;285(50):39564-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.177055. Epub 2010 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20923770 Free PMC article.
-
The response to iron deprivation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: expression of siderophore-based systems of iron uptake.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Aug;30(4):698-702. doi: 10.1042/bst0300698. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12196168 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cation balance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2013 Mar;193(3):677-713. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.147207. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23463800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FgEnd1 is a putative component of the endocytic machinery and mediates ferrichrome uptake in F. graminearum.Curr Genet. 2009 Dec;55(6):593-600. doi: 10.1007/s00294-009-0272-8. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Curr Genet. 2009. PMID: 19756628
-
Fungal-Metal Interactions: A Review of Toxicity and Homeostasis.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;7(3):225. doi: 10.3390/jof7030225. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural requirements for the activity of the MirB ferrisiderophore transporter of Aspergillus fumigatus.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Nov;11(11):1333-44. doi: 10.1128/EC.00159-12. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22903978 Free PMC article.
-
Host iron withholding demands siderophore utilization for Candida glabrata to survive macrophage killing.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Mar;7(3):e1001322. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001322. Epub 2011 Mar 17. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21445236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson J, Smirnova I, Kasho V, Verner G, Iwata S, Kaback HR (2003a) The lactose permease of Escherichia coli: overall structure, the sugar-binding site and the alternating access model for transport. FEBS Lett 555: 96–101 - PubMed
-
- Abramson J, Smirnova I, Kasho V, Verner G, Kaback HR, Iwata S (2003b) Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science 301: 610–615 - PubMed
-
- Aridor M, Traub LM (2002) Cargo selection in vesicular transport: the making and breaking of a coat. Traffic 3: 537–546 - PubMed
-
- Askwith C, Eide D, Van Ho A, Bernard PS, Li L, Davis-Kaplan S, Sipe DM, Kaplan J (1994) The FET3 gene of S. cerevisiae encodes a multicopper oxidase required for ferrous iron uptake. Cell 76: 403–410 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

