Calcium-independent calmodulin binding and two-metal-ion catalytic mechanism of anthrax edema factor
- PMID: 15719022
- PMCID: PMC554124
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600574
Calcium-independent calmodulin binding and two-metal-ion catalytic mechanism of anthrax edema factor
Abstract
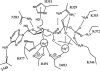
Edema factor (EF), a key anthrax exotoxin, has an anthrax protective antigen-binding domain (PABD) and a calmodulin (CaM)-activated adenylyl cyclase domain. Here, we report the crystal structures of CaM-bound EF, revealing the architecture of EF PABD. CaM has N- and C-terminal domains and each domain can bind two calcium ions. Calcium binding induces the conformational change of CaM from closed to open. Structures of the EF-CaM complex show how EF locks the N-terminal domain of CaM into a closed conformation regardless of its calcium-loading state. This represents a mechanism of how CaM effector alters the calcium affinity of CaM and uncouples the conformational change of CaM from calcium loading. Furthermore, structures of EF-CaM complexed with nucleotides show that EF uses two-metal-ion catalysis, a prevalent mechanism in DNA and RNA polymerases. A histidine (H351) further facilitates the catalysis of EF by activating a water to deprotonate 3'OH of ATP. Mammalian adenylyl cyclases share no structural similarity with EF and they also use two-metal-ion catalysis, suggesting the catalytic mechanism-driven convergent evolution of two structurally diverse adenylyl cyclases.
Figures

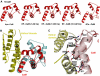




References
-
- Aqvist J, Medina C, Samuelson JE (1994) A new model for predicting binding affinity in computer-aided drug design. Protein Eng 7: 385–391 - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, Kelly JM (2004) Structure, function and evolution of microbial adenylyl and guanylyl cyclases. Mol Microbiol 52: 1229–1242 - PubMed
-
- Barford D, Das AK, Egloff MP (1998) The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 27: 133–164 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya S, Bunick CG, Chazin WJ (2004) Target selectivity in EF-hand calcium binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1742: 69–79 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

