Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signalling and T-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 15720432
- PMCID: PMC1782085
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02091.x
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signalling and T-cell lymphomas
Abstract
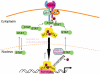
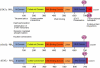
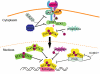
Interaction of cytokines with their cognate receptors leads to the activation of latent transcription factors - the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins - whose biological activities ultimately regulate many critical aspects of cell growth, survival and differentiation. Dysregulation of the JAK-STAT pathway is frequently observed in many primary human tumours, reflecting the importance of this pathway in the maintenance of cellular integrity. Here we review the current progress in STAT structure and function, and the contribution of STAT signalling to the pathogenesis of T-cell lymphomas.
Figures
References
-
- Darnell JE, Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264:1415. - PubMed
-
- Gadina M, Hilton D, Johnston JA, Morinobu A, Lighvani A, Zhou YJ, Visconti R, O'Shea JJ. Signaling by type I and II cytokine receptors: ten years after. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001;13:363. - PubMed
-
- Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, Jove R. STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2000;19:2474. - PubMed
-
- Calo V, Migliavacca M, Bazan V, Macaluso M, Buscemi M, Gebbia N, Russo A. STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2003;197:157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

