Lupus autoantibodies to native DNA preferentially bind DNA presented on PolIV
- PMID: 15720443
- PMCID: PMC1782086
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02090.x
Lupus autoantibodies to native DNA preferentially bind DNA presented on PolIV
Abstract
While immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies to double-stranded (ds)DNA are serological markers of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), not all antibodies to DNA (anti-DNA) are able to cause tissue damage to a similar extent. It has been proposed that anti-DNA-induced renal damage could be linked to differences in the fine specificity of the antibodies. In an attempt to gain insight into their fine binding properties, we investigated the cross-reactivity of two human lupus monoclonal IgG anti-dsDNA (B3 and RH14) to a recently described Escherichia coli PolIV (a DNA polymerase). These autoantibodies possess distinct pathogenic properties in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. Although both antibodies cause proteinuria, only RH14 induces early histological features of lupus nephritis. Both RH14 and B3 bound PolIV; however, they exhibited a marked difference in their reactivity to the PolIV-dsDNA complex. Alhough RH14 exhibited significant activity to the complex, the binding of B3 to PolIV complexed with dsDNA was almost abolished. Furthermore, there was a significant difference in the way the lupus sera recognized naked dsDNA and that presented on PolIV. Although 67% of lupus sera bound naked dsDNA, approximately 90% of these sera (93% calf thymus DNA; 90% synthetic oligonucleotide) reacted to the complex when dsDNA was presented on PolIV. Thus, the IgG anti-dsDNA likely to exist in lupus patients may be distinguished into those that recognize dsDNA in the context of PolIV and those which do not. This difference in binding ability may help to distinguish those dsDNA antibodies that are more pathogenic.
Figures
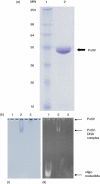




References
-
- Swaak AJG, Aarden LA, Statius van Eps LW, Feltkamp TE. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979;22:226–35. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg DA, Garton M, Reichlin MW, Reichlin M. Long-term follow-up of autoantibody profiles in black female lupus patients and clinical comparison with Caucasian and Asian patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1997;36:229–33. - PubMed
-
- Okamura M, Kanayama Y, Amastu K, Negoro N, Kohda S, Takeda T, Inoue T. Significance of enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) for antibodies to double stranded and single stranded DNA in patients with lupus nephritis: correlation with severity of renal histology. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993;52:14–20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Isenberg DA, Shoenfeld Y, Walport M, et al. Detection of cross-reactive anti-DNA antibody idiotypes in the serum of systemic lupus erythematosus patients and of their relatives. Arthritis Rheum. 1985;28:999–1007. - PubMed
-
- Cabral AR, Alarcon-Segovia D. Autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1997;9:387–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

