Overexpression of 12/15-lipoxygenase, an ortholog of human 15-lipoxygenase-1, in the prostate tumors of TRAMP mice
- PMID: 15720809
- PMCID: PMC1531686
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04286
Overexpression of 12/15-lipoxygenase, an ortholog of human 15-lipoxygenase-1, in the prostate tumors of TRAMP mice
Abstract
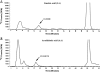
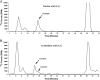
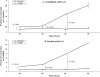
Changes in the expression and activity of lipid-metabolizing enzymes, including the linoleic acid (LA)-metabolizing enzyme 15-lipoxygenase-1 (15-LO-1), may play a role in the development and progression of human prostate carcinoma (PCa). We reported that human 15-LO-1 (designated as leukocyte type 12-LO or 12/15-LO in mouse) is expressed in human prostate and increased in PCa, particularly high-grade PCa. Genetically engineered mouse (GEM) models of PCa could facilitate the study of this gene and its regulation and function in PCa progression. In this study, we examine the protein expression and enzyme activity levels of 12/15-LO associated with PCa progression in the TRansgenic Adenocarcinoma of Mouse Prostate (TRAMP) model of PCa. This GEM model develops prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN), followed by invasive gland-forming PCa and invasive and metastatic less differentiated PCa, with neuroendocrine (NE) differentiation (NE Ca). In the wild-type and TRAMP prostates, the most prominent LA metabolite was 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE). Lesser amounts of 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid and 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE) were made from arachidonic acid (AA). In TRAMP prostates, 12/15-LO activity was increased compared to wild type at 20, 29, 39, and 49 weeks, as assessed by LA conversion to 13-HODE, and by AA conversion to 12/15-HETE, respectively. Immunostaining demonstrated that the increased capacity to generate 13-HODE was paralleled by an increase in neoplastic epithelial expression of 12/15-LO in PIN and invasive carcinomas. In conclusion, although there is a basal 12/15-LO activity in the wild-type mouse prostate, there is a marked increase in the expression of 12/15-LO with TRAMP PCa progression, paralleling our previously reported increased expression of the ortholog 15-LO-1 in high-grade human PCa. Thus, 12/15-LO and LA metabolism in the TRAMP model shares similarities to human PCa, and may allow to confirm a role for LA metabolism and other biologic functions of 15-LO-1 in human PCa. In addition, the TRAMP model will serve as a tool for testing the suitability of 12/15-LO-and ultimately human 15-LO--as a therapeutic target during PCa progression.
Figures

References
-
- Shappell SB, Thomas GV, Roberts RL, Herbert R, Ittmann MM, Rubin MA, Humphrey PA, Sundberg JP, Rozengurt N, Barrios R, Ward JM, Cardiff RD. Prostate pathology of genetically engineered mice: definitions and classification. The consensus report from the Bar Harbor meeting of the Mouse Models of Human Cancer Consortium Prostate Pathology Committee. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2270–2305. - PubMed
-
- Wechter WJ, Leipold DD, Murray ED, Jr, Quiggle D, McCracken JD, Barrios RS, Greenberg NM. E-7869 (R-flurbiprofen) inhibits progression of prostate cancer in the TRAMP mouse. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2203–2208. - PubMed
-
- Mentor-Marcel R, Lamartiniere CA, Eltoum IE, Greenberg NM, Elgavish A. Genistein in the diet reduces the incidence of poorly differentiated prostatic adenocarcinoma in transgenic mice (TRAMP) Cancer Res. 2001;61:6777–67782. - PubMed
-
- Abate-Shen C, Shen MM. Mouse models of prostate carcinogenesis. Trends Genet. 2002;18:S1–S5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
