Phosphorylation of both EGFR and ErbB2 is a reliable predictor of prostate cancer cell proliferation in response to EGF
- PMID: 15720812
- PMCID: PMC1531689
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04379
Phosphorylation of both EGFR and ErbB2 is a reliable predictor of prostate cancer cell proliferation in response to EGF
Abstract
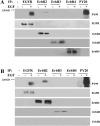
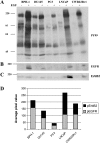
Despite multiple reports of overexpression in prostate cancer (PC), the reliance of PC cells on activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its downstream signaling to phosphoinositide 3'-kinase/Akt (PI3K/Akt/PTEN) and/or mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK) pathways has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we compared the role of EGF-mediated signaling in nonmalignant (BPH-1, PNT1A, and PNT1B) and PC cell lines (DU145, PC3, LNCaP, and CWR22Rv1). EGF-induced proliferation was observed in all EGFR-expressing PC cells except PC3, indicating that EGFR expression does not unequivocally trigger proliferation following EGF stimulation. ErbB2 recruitment potentiated EGF-induced signals and was associated with the most pronounced effects of EGF despite low EGFR expression. In this way, the sum of EGFR and ErbB2 receptor phosphorylation proved to be a more sensitive indicator of EGF-induced proliferation than quantification of the expression of either receptor alone. Both Akt and ERK were rapidly phosphorylated in response to EGF, with ERK phosphorylation being the weakest in PC3 cells. Extrapolation of these findings to clinical PC suggests that assessment of phosphorylated EGFR + ErbB2 together could serve as a marker for sensitivity to anti-EGFR-targeted therapies.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor, c-erbB2 and c-erbB3 receptor interaction, and related cell cycle kinetics of SK-BR-3 and BT474 breast carcinoma cells.Cytometry. 2001 Aug 1;44(4):338-48. doi: 10.1002/1097-0320(20010801)44:4<338::aid-cyto1125>3.0.co;2-v. Cytometry. 2001. PMID: 11500850
-
Gefitinib ('IRESSA', ZD1839) inhibits EGF-induced invasion in prostate cancer cells by suppressing PI3 K/AKT activation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004 Oct;130(10):604-14. doi: 10.1007/s00432-004-0581-8. Epub 2004 Jul 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15258753 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity to gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines correlates with dependence on the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and EGF receptor/Akt pathway for proliferation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Apr;3(4):465-72. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004. PMID: 15078990
-
Blockade of epidermal growth factor- or heregulin-dependent ErbB2 activation with the anti-ErbB2 monoclonal antibody 2C4 has divergent downstream signaling and growth effects.Cancer Res. 2004 Apr 1;64(7):2601-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3106. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15059917
-
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor kinase-independent signaling by EGF.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 4;276(18):15554-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100928200. Epub 2001 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11279155
Cited by
-
Matriptase is involved in ErbB-2-induced prostate cancer cell invasion.Am J Pathol. 2010 Dec;177(6):3145-58. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100228. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20971737 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-EGFR antibody conjugated organic-inorganic hybrid lipid nanovesicles selectively target tumor cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014 Sep 1;121:141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014. PMID: 24967549 Free PMC article.
-
A transductionally retargeted adenoviral vector for virotherapy of Her2/neu-expressing prostate cancer.Hum Gene Ther. 2012 Jan;23(1):70-82. doi: 10.1089/hum.2011.016. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Hum Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 21875358 Free PMC article.
-
Prostasin induces protease-dependent and independent molecular changes in the human prostate carcinoma cell line PC-3.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jul;1773(7):1133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.04.013. Epub 2007 May 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17532063 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronan suppresses prostate tumor cell proliferation through diminished expression of N-cadherin and aberrant growth factor receptor signaling.Exp Cell Res. 2011 May 1;317(8):1214-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.01.026. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21315068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barton J, Blackledge G, Wakeling A. Growth factors and their receptors: new targets for prostate cancer therapy. Urology. 2001;58:114–122. - PubMed
-
- George DJ. Receptor tyrosine kinases as rational targets for prostate cancer treatment: platelet-derived growth factor receptor and imatinib mesylate. Urology. 2002;60:115–121. discussion, 122. - PubMed
-
- Grasso AW, Wen D, Miller CM, Rhim JS, Pretlow TG, Kung HJ. ErbB kinases and NDF signaling in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:2705–2716. - PubMed
-
- Kim HG, Kassis J, Souto JC, Turner T, Wells A. EGF receptor signaling in prostate morphogenesis and tumorigenesis. Histol Histopathol. 1999;14:1175–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Hung MC, Weinberg RA. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986;45:649–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
