Randomised controlled trial of sub-Tenon's block versus topical anaesthesia for cataract surgery: a comparison of patient satisfaction
- PMID: 15722306
- PMCID: PMC1772574
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2004.052167
Randomised controlled trial of sub-Tenon's block versus topical anaesthesia for cataract surgery: a comparison of patient satisfaction
Abstract
Background/aim: Sub-Tenon's block (STB) or topical anaesthesia alone (TOP) are popular techniques employed during cataract surgery. TOP is often preferred by healthcare providers because of financial or staffing reasons, despite existing evidence that pain during surgery is better controlled with STB. Pain is not the only consideration that determines patient preference for the anaesthesia technique. The authors decided to investigate the issue of patient satisfaction using the recently developed Iowa Satisfaction with Anesthesia Scale (ISAS).
Method: In a randomised controlled pilot trial, 28 patients were enrolled to receive either STB with 3 ml of 2% lidocaine and hyaluronidase, or TOP with proxymetacaine 0.5% and amethocaine 1% (Tetracaine) eye drops. Postoperatively patients rated their satisfaction with anaesthesia care by filling in the self administered written questionnaire, the ISAS.
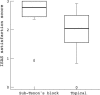
Results: One patient in the TOP group dropped out of the study because of intolerable pain. Analysis of the questionnaire results with a two sample Wilcoxon rank sum test showed a significant difference in patient satisfaction (p<0.0085). The median satisfaction score was higher in the STB group 2.77 (interquartile range IQR 2.45 to 3), than in the TOP group 2.04 (IQR 1.54 to 2.5).
Conclusion: In the setting of day case cataract surgery, patients report significantly higher satisfaction scores with STB than with TOP alone.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is one trial enough?Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Apr;89(4):398. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2004.055517. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15774911 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sub-Tenon's block versus topical anaesthesia for cataract surgery.Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Sep;89(9):1227-8. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.073858. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 16113392 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Patient satisfaction with anaesthesia comparing sub-Tenon's block and topical anaesthesia.Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Sep;89(9):1228. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.075895. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 16113395 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Friedman DS, Bass EB, Lubomski LH. Synthesis of the literature on the effectiveness of regional anesthesia for cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 2001;108:519–29. - PubMed
-
- Manners TD, Burton RL. Randomised trial of topical versus sub-Tenon’s local anaesthesia for small-incision cataract surgery [see comments]. Eye 1996;10 (Pt 3) :367–70. - PubMed
-
- Zafirakis P, Voudouri A, Rowe S, et al. Topical versus sub-Tenon’s anesthesia without sedation in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001;27:873–9. - PubMed
-
- Dexter F, Aker J, Wright WA. Development of a measure of patient satisfaction with monitored anesthesia care: the Iowa Satisfaction with Anesthesia Scale. Anesthesiology 1997;87:865–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources