Sterol structure determines the separation of phases and the curvature of the liquid-ordered phase in model membranes
- PMID: 15722414
- PMCID: PMC552914
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408215102
Sterol structure determines the separation of phases and the curvature of the liquid-ordered phase in model membranes
Abstract
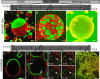
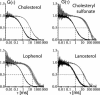
The existence of lipid rafts in biological membranes in vivo is still debated. In contrast, the formation of domains in model systems has been well documented. In giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) prepared from ternary mixtures of dioleoyl-phosphatidylcholine/sphingomyelin/cholesterol, a clear separation of liquid-disordered and sphingomyelin-enriched, liquid-ordered phases could be observed. This phase separation can lead to the fission of the liquid-ordered phase from the vesicle. Here we show that in cholesterol-containing GUVs, the phase separation can involve dynamic redistribution of lipids from one phase into another as a result of a cross-linking perturbation. We found that the molecular structure of a sterol used for the preparation of GUVs determines (i) its ability to induce phase separation and (ii) the curvature (positive or negative) of the formed liquid-ordered phase. As a consequence, the latter can pinch off to the outside or inside of the vesicle. Remarkably, some mixtures of sterols induce liquid-ordered domains exhibiting both positive and negative curvature, which can lead to a new type of budding behavior in GUVs. Our findings could have implications for the role of sterols in various cell-biological processes such as budding of secretory vesicles, endocytosis, or formation of multivesicular bodies.
Figures


References
-
- Simons, K. & Ikonen, E. (1997) Nature 387, 569-572. - PubMed
-
- Simons, K. & Toomre, D. (2000) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 31-39. - PubMed
-
- Recktenwald, D. J. & McConnell, H. M. (1981) Biochemistry 20, 4505-4510. - PubMed
-
- Ipsen, J. H., Karlstrom, G., Mouritsen, O. G., Wennerstrom, H. & Zuckermann, M. J. (1987) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 905, 162-172. - PubMed
-
- Sankaram, M. B. & Thompson, T. E. (1990) Biochemistry 29, 10670-10675. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

