RIN13 is a positive regulator of the plant disease resistance protein RPM1
- PMID: 15722472
- PMCID: PMC1069715
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.104.028720
RIN13 is a positive regulator of the plant disease resistance protein RPM1
Abstract
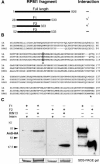
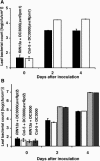
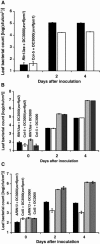
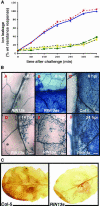
The RPM1 protein confers resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000 expressing either of the Type III effector proteins AvrRpm1 or AvrB. Here, we describe the isolation and functional characterization of RPM1 Interacting Protein 13 (RIN13), a resistance protein interactor shown to positively enhance resistance function. Ectopic expression of RIN13 (RIN13s) enhanced bacterial restriction mechanisms but paradoxically abolished the normally rapid hypersensitive response (HR) controlled by RPM1. In contrast with wild-type plants, leaves expressing RIN13s did not undergo electrolyte leakage or accumulate H2O2 after bacterial delivery of AvrRpm1. Overexpression of RIN13 also altered the transcription profile observed during a normal HR. By contrast, RIN13 knockout plants had the same ion leakage signatures and HR timing of wild-type plants in response to DC3000(avrRpm1) but failed to suppress bacterial growth. The modified phenotypes seen in the RIN13s/as plants were specific to recognition of AvrRpm1 or AvrB, and wild-type responses were observed after challenge with other incompatible pathogens or the virulent DC3000 isolate. Our results suggest that cell death is not necessary to confer resistance, and engineering enhanced resistance without activation of programmed cell death is a real possibility.
Figures



References
-
- Adams, J.M., and Cory, S. (2002). Apoptosomes: Engines for caspase activation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 715–720. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301, 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L., Dixit, V.M., and Koonin, E.V. (1999). The domains of death: Evolution of the apoptosis machinery. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 47–53. - PubMed
-
- Axtell, M.J., and Staskawicz, B.J. (2003). Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112, 369–377. - PubMed
-
- Balague, C., Lin, B., Alcon, C., Flottes, G., Malmstrom, S., Kohler, C., Neuhaus, G., Pelletier, G., Gaymard, F., and Roby, D. (2003). HLM1, an essential signaling component in the hypersensitive response, is a member of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel ion channel family. Plant Cell 15, 365–379. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

