Inhibition of granuloma-associated angiogenesis by controlling mast cell mediator release: role of mast cell protease-5
- PMID: 15723097
- PMCID: PMC1576110
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706112
Inhibition of granuloma-associated angiogenesis by controlling mast cell mediator release: role of mast cell protease-5
Abstract
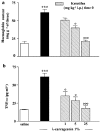
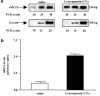
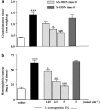
We investigated the role of mast cells in granuloma-associated angiogenesis in rat by using: (i) a mast cell membrane stabilizer, ketotifen; (ii) a mast cell depleting agent, compound 48/80. Moreover, we focused on the role of chymases, which exhibit proinflammatory and pro-angiogenic properties by using: (i) chymostatin, an inhibitor of chymase activity; (ii) a specific antisense oligonucleotide (AS-ODN) designed against rat mast cell protease-5 (rMCP-5), the most abundantly expressed chymase in the skin. The formation of granuloma was evaluated, as wet weight, 96 h after the subcutaneous implant of two lambda-carrageenin (1%)-soaked sponges on the back of male Wistar rats. Angiogenesis was evaluated as haemoglobin content in the granulomatous tissue and as level of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in the exudates. A single injection of ketotifen (1-5-25 mg kg(-1) i.p.) significantly reduced granuloma formation by 31.6, 44.6 and 71.9%, and haemoglobin content by 17.0, 35.0 and 66.2%, suggesting that the release of mediator(s) from mast cells modulates the process. Chymostatin (5-10 nmol(-1) site(-1) day(-1)) reduced granuloma-associated angiogenesis by 57.3 and 70.0%. RT-PCR analysis showed that rMCP-5 mRNA amounts were significantly reduced by rMCP-5 AS-ODN (1.25-2.5-5.0 nmol site(-1)) by 69.5, 72.5 and 81.8%. In parallel experiments, rMCP-5 AS-ODN (1.25, 2.5, 5.0 nmol site(-1)) strongly reduced granuloma weight (26.1, 45.0 and 56.3%) and haemoglobin content (22.2, 50.4, 62.03%), suggesting that the observed effect is mediated through an antisense mechanism. In conclusion, these data suggest that: (i) inhibition of mast cell mediators release may represent a novel strategy to modulate angiogenesis; (ii) among the chymase family, rMCP-5 is a key promoter of angiogenesis in the rat.
Figures

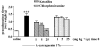
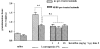


References
-
- BREIER G., ALBRECHT U., STERRER S., RISAU W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992;114:524–532. - PubMed
-
- CHANDRASEKHARAN U.M., SANKER S., GLYNIAS M.Y., KARNIK S.S., HUSAIN A. Angiotensin II-forming activity in a reconstructed ancestral chymase. Science. 1996;271:502–505. - PubMed
-
- COLVILLE-NASH P.R., ALAM C.A.S., APPLETON I., BROWN J.R., SEED M., WILLOUGHBY D.A. The pharmacological modulation of angiogenesis in chronic granulomatous inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995;274:1463–1471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

