Principles of microRNA-target recognition
- PMID: 15723116
- PMCID: PMC1043860
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030085
Principles of microRNA-target recognition
Abstract
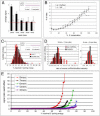
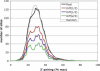
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression in plants and animals. Although their biological importance has become clear, how they recognize and regulate target genes remains less well understood. Here, we systematically evaluate the minimal requirements for functional miRNA-target duplexes in vivo and distinguish classes of target sites with different functional properties. Target sites can be grouped into two broad categories. 5' dominant sites have sufficient complementarity to the miRNA 5' end to function with little or no support from pairing to the miRNA 3' end. Indeed, sites with 3' pairing below the random noise level are functional given a strong 5' end. In contrast, 3' compensatory sites have insufficient 5' pairing and require strong 3' pairing for function. We present examples and genome-wide statistical support to show that both classes of sites are used in biologically relevant genes. We provide evidence that an average miRNA has approximately 100 target sites, indicating that miRNAs regulate a large fraction of protein-coding genes and that miRNA 3' ends are key determinants of target specificity within miRNA families.
Figures

References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Lai EC. microRNAs: Runts of the genome assert themselves. Curr Biol. 2003;13:R925–R936. - PubMed
-
- Carrington JC, Ambros V. Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science. 2003;301:336–338. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature. 2000;408:86–89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

