Extraction of overt verbal response from the acoustic noise in a functional magnetic resonance imaging scan by use of segmented active noise cancellation
- PMID: 15723385
- PMCID: PMC3591487
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.20398
Extraction of overt verbal response from the acoustic noise in a functional magnetic resonance imaging scan by use of segmented active noise cancellation
Abstract
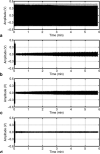
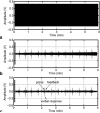
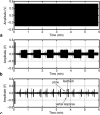
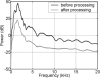
A method to extract the subject's overt verbal response from the obscuring acoustic noise in an fMRI scan is developed by applying active noise cancellation with a conventional MRI microphone. Since the EPI scanning and its accompanying acoustic noise in fMRI are repetitive, the acoustic noise in one time segment was used as a reference noise in suppressing the acoustic noise in subsequent segments. However, the acoustic noise from the scanner was affected by the subject's movements, so the reference noise was adaptively adjusted as the scanner's acoustic properties varied in time. This method was successfully applied to a cognitive fMRI experiment with overt verbal responses.
(c) 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
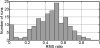
References
-
- Schmitt F, Stehling MK, Turner R. Echo-planar imaging theory, technique, and application. Springer; New York: 1998.
-
- Cho ZH, Park SH, Kim JH, Chung SC, Chung ST, Chung JY, Moon CW, Yi JH, Sin CH, Wong EK. Analysis of acoustic noise in MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 1997;15:815–822. - PubMed
-
- Phelps EA, Hyder F, Blamire AM, Shulman RG. FMRI of the prefrontal cortex during overt verbal fluency. Neuroreport. 1997;8:561–565. - PubMed
-
- Schlaggar BL, Brown TT, Lugar HM, Visscher KM, Miezin FM, Petersen SE. Functional neuroanatomical differences between adults and school-age children in the processing of single words. Science. 2002;296:1476–1479. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JR, Qin Y, Stenger VA, Carter CS. The relationship of three cortical regions to an information-processing model. Cogn Neurosci. 2004;16:637–653. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

