Role of nitrosative stress and peroxynitrite in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Emerging new therapeutical strategies
- PMID: 15723618
- PMCID: PMC2225483
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867053363207
Role of nitrosative stress and peroxynitrite in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Emerging new therapeutical strategies
Abstract
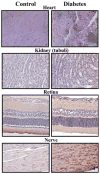
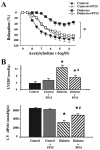
Macro- and microvascular disease are the most common causes of morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic cardiovascular dysfunction represents a problem of great clinical importance underlying the development of various severe complications including retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy and increase the risk of stroke, hypertension and myocardial infarction. Hyperglycemic episodes, which complicate even well-controlled cases of diabetes, are closely associated with increased oxidative and nitrosative stress, which can trigger the development of diabetic complications. Hyperglycemia stimulates the production of advanced glycosylated end products, activates protein kinase C, and enhances the polyol pathway leading to increased superoxide anion formation. Superoxide anion interacts with nitric oxide, forming the potent cytotoxin peroxynitrite, which attacks various biomolecules in the vascular endothelium, vascular smooth muscle and myocardium, leading to cardiovascular dysfunction. The pathogenetic role of nitrosative stress and peroxynitrite, and downstream mechanisms including poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation, is not limited to the diabetes-induced cardiovascular dysfunction, but also contributes to the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy. Accordingly, neutralization of peroxynitrite or pharmacological inhibition of PARP is a promising new approach in the therapy and prevention of diabetic complications. This review focuses on the role of nitrosative stress and downstream mechanisms including activation of PARP in diabetic complications and on novel emerging therapeutical strategies offered by neutralization of peroxynitrite and inhibition of PARP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of peroxynitrite in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular complications of diabetes.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006 Apr;6(2):136-41. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16483848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathogenesis of diabetic complications: the role of DNA injury and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in peroxynitrite-mediated cytotoxicity.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2005 Mar;100 Suppl 1:29-37. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762005000900007. Epub 2005 Jun 14. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2005. PMID: 15962096 Review.
-
Role of nitrosative stress and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in diabetic vascular dysfunction.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;3(3):247-52. doi: 10.2174/1570161054368571. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16026321 Review.
-
Role for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation in diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy and retinopathy.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;3(3):267-83. doi: 10.2174/1570161054368634. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16026323 Review.
-
Role of redox signaling and poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase activation in vascular smooth muscle cell growth inhibition by nitric oxide and peroxynitrite.J Vasc Surg. 2008 Mar;47(3):599-607. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.11.006. J Vasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 18295111
Cited by
-
Visfatin/Nampt: an adipokine with cardiovascular impact.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:946427. doi: 10.1155/2013/946427. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23843684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathies as complications of diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Feb 28;8(7):405-16. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.21. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22371159 Review.
-
Reno-protective effects of Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021 Jun;25(6):585-597. doi: 10.1007/s10157-021-02051-6. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33754203 Review.
-
Nature and Implications of Oxidative and Nitrosative Stresses in Autoimmune Hepatitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Oct;61(10):2784-2803. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4247-6. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27411555 Review.
-
The Anti-nociceptive Effect of Ellagic Acid in Streptozotocin-induced Hyperglycemic Rats by Oxidative Stress Involvement.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2021 Nov-Dec;12(6):861-872. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2021.2413.1. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 35693147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brownlee M. Nature. 2001;14:813–820. - PubMed
-
- Ceriello A. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1589–1596. - PubMed
-
- Ruderman NB, Williamson JR, Brownlee M. FASEB J. 1992;6:2905–2914. - PubMed
-
- Hoeldtke RD. Clin Auton Res. 2003;13(6):406–421. - PubMed
-
- Nagai R, Unno Y, Hayashi MC, Masuda S, Hayase F, Kinae N, Horiuchi S. Diabetes. 2002;51(9):2833–2839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

