STI571 (Glivec) inhibits the interaction between c-KIT and heat shock protein 90 of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell line, GIST-T1
- PMID: 15723656
- PMCID: PMC11158277
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00018.x
STI571 (Glivec) inhibits the interaction between c-KIT and heat shock protein 90 of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell line, GIST-T1
Abstract
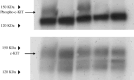
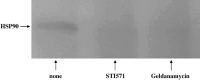
The gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell line, GIST-T1, has a heterogenic 57-base pair deletion in exon 11 of the c-kit mutation, and the c-KIT protein in the GIST-T1 cells constitutively activated. We report that STI571 (Glivec; Novartis, Basel, Switzerland), a specific inhibitor of c-KIT, inhibits the clustering of c-KIT at the cell membrane of the GIST-T1 cells. Furthermore, STI571 prevents the interaction between c-KIT and the molecular chaperone, heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). Geldanamycin, an inhibitor of Hsp90, also prevents interaction between c-KIT and Hsp90, and inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of c-KIT. Our results indicate that c-KIT molecules are assembled on the cell surface of the GIST-T1 cells, and that the interaction between c-KIT and Hsp90 plays an important role in c-KIT activation.
Figures

References
-
- Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Kanakura Y, Nishida T, Ishigro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M, Tunio GM, Matsuzawa Y, Shinomura Y, Kitamura Y. Gain‐of‐function mutation of c‐kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 1998; 279: 577–80. - PubMed
-
- Nishida T, Hirota S. Biological and clinical review of stromal tumors in the gastrointestinal tract. Histol Histopathol 2000; 4: 1293–301. - PubMed
-
- Galli SJ, Zsebo KM, Geissler EN. The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv Immunol 1994; 55: 1–96. - PubMed
-
- Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A. W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 1995; 373: 347–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

