Platelet-derived growth factor C induces liver fibrosis, steatosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 15728360
- PMCID: PMC552940
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409722102
Platelet-derived growth factor C induces liver fibrosis, steatosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
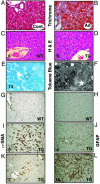
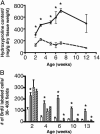
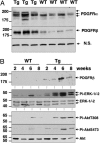
Members of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) ligand family are known to play important roles in wound healing and fibrotic disease. We show that both transient and stable expression of PDGF-C results in the development of liver fibrosis consisting of the deposition of collagen in a pericellular and perivenular pattern that resembles human alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Fibrosis in PDGF-C transgenic mice, as demonstrated by staining and hydroxyproline content, is preceded by activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells, as shown by collagen, alpha-smooth muscle actin and glial fibrillary acidic protein staining and between 8 and 12 months of age is followed by the development of liver adenomas and hepatocellular carcinomas. The hepatic expression of a number of known profibrotic genes, including type beta1 TGF, PDGF receptors alpha and beta, and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases-1 and -2, increased by 4 weeks of age. Increased PDGF receptor alpha and beta protein levels were associated with activation of extracellular regulated kinase-1 and -2 and protein kinase B. At 9 months of age, PDGF-C transgenic mice had enlarged livers associated with increased fibrosis, steatosis, cell dysplasia, and hepatocellular carcinomas. These studies indicate that hepatic expression of PDGF-C induces a number of profibrotic pathways, suggesting that this growth factor may act as an initiator of fibrosis. Moreover, PDGF-C transgenic mice represent a unique model for the study of hepatic fibrosis progressing to tumorigenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Bedossa, P. & Paradis, V. (2003) J. Pathol. 200, 504-515. - PubMed
-
- Rojkind, M., Giambrone, M. A. & Biempica, L. (1979) Gastroenterology 76, 710-719. - PubMed
-
- Milani, S., Herbst, H., Schuppan, D., Hahn, E. G. & Stein, H. (1989) Hepatology 10, 84-92. - PubMed
-
- Friedman, S. L. (1997) Gastroenterology 112, 1406-1409. - PubMed
-
- Hui, A. Y. & Friedman, S. L. (2003) Exp. Rev. Mol. Med. 2003, 1-23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

