Matrix metalloproteinase 13 mediates nitric oxide activation of endothelial cell migration
- PMID: 15728377
- PMCID: PMC553299
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408217102
Matrix metalloproteinase 13 mediates nitric oxide activation of endothelial cell migration
Abstract
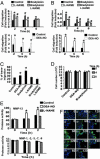
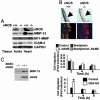
To explore the mechanisms by which NO elicits endothelial cell (EC) migration we used murine and bovine aortic ECs in an in vitro wound-healing model. We found that exogenous or endogenous NO stimulated EC migration. Moreover, migration was significantly delayed in ECs derived from endothelial NO synthase-deficient mice compared with WT murine aortic EC. To assess the contribution of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 to NO-mediated EC migration, we used RNA interference to silence MMP-13 expression in ECs. Migration was delayed in cells in which MMP-13 was silenced. In untreated cells MMP-13 was localized to caveolae, forming a complex with caveolin-1. Stimulation with NO disrupted this complex and significantly increased extracellular MMP-13 abundance, leading to collagen breakdown. Our findings show that MMP-13 is an important effector of NO-activated endothelial migration.
Figures




References
-
- Schwentker, A., Vodovotz, Y., Weller, R. & Billiar, T. R. (2002) Nitric Oxide 7, 1-10. - PubMed
-
- Dimmeler, S., Dernbach, E. & Zeiher, A. M. (2000) FEBS Lett. 477, 258-262. - PubMed
-
- Noiri, E., Lee, E., Testa, J., Quigley, J., Colflesh, D., Keese, C. R., Giaever, I. & Goligorsky, M. S. (1998) Am. J. Physiol. 274, C236-C244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

