Thyroxine-binding antibodies inhibit T cell recognition of a pathogenic thyroglobulin epitope
- PMID: 15728526
- PMCID: PMC2583135
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.5.3105
Thyroxine-binding antibodies inhibit T cell recognition of a pathogenic thyroglobulin epitope
Abstract
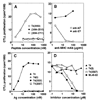
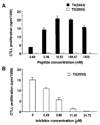
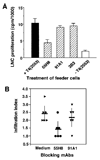
Thyroid hormone-binding (THB) Abs are frequently detected in autoimmune thyroid disorders but it is unknown whether they can exert immunoregulatory effects. We report that a THB mAb recognizing the 5' iodine atom of the outer phenolic ring of thyroxine (T4) can block T cell recognition of the pathogenic thyroglobulin (Tg) peptide (2549-2560) that contains T4 at aa position 2553 (T4(2553)). Following peptide binding to the MHC groove, the THB mAb inhibited activation of the A(k)-restricted, T4(2553)-specific, mouse T cell hybridoma clone 3.47, which does not recognize other T4-containing epitopes or noniodinated peptide analogues. Addition of the same THB mAb to T4(2553)-pulsed splenocytes largely inhibited specific activation of T4(2553)-primed lymph node cells and significantly reduced their capacity to adoptively transfer thyroiditis to naive CBA/J mice. These data demonstrate that some THB Abs can block recognition of iodine-containing Tg epitopes by autoaggressive T cells and support the view that such Abs may influence the development or maintenance of thyroid disease.
Figures



References
-
- Benvenga S, Trimarchi F, Robbins J. Circulating thyroid hormone autoantibodies. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 1987;10:605. - PubMed
-
- Sakata S. Autoimmunity against thyroid hormones. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 1994;14:157. - PubMed
-
- Despres N, Grant AM. Antibody interference in thyroid assays: a potential for clinical misinformation. Clin. Chem. 1998;44:440. - PubMed
-
- Sapin R, Gasser F, Boehn A, Rondeau M. Spuriously high concentration of serum free thyroxine due to anti-triiodothyronine antibodies. Clin. Chem. 1995;41:117. - PubMed
-
- Shimon I, Pariente C, Shlomo-David J, Grossman Z, Sack J. Transient elevation of triiodothyronine caused by triiodothyronine autoantibody associated with acute Epstein-Barr-virus infection. Thyroid. 2003;13:211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

