Tonotopic specialization of auditory coincidence detection in nucleus laminaris of the chick
- PMID: 15728832
- PMCID: PMC6726073
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4428-04.2005
Tonotopic specialization of auditory coincidence detection in nucleus laminaris of the chick
Abstract
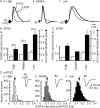
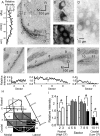
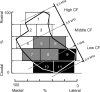
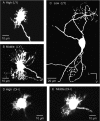
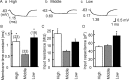
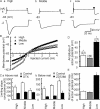
The interaural time difference (ITD) is a cue for localizing a sound source along the horizontal plane and is first determined in the nucleus laminaris (NL) in birds. Neurons in NL are tonotopically organized, such that ITDs are processed separately at each characteristic frequency (CF). Here, we investigated the excitability and coincidence detection of neurons along the tonotopic axis in NL, using a chick brainstem slice preparation. Systematic changes with CF were observed in morphological and electrophysiological properties of NL neurons. These properties included the length of dendrites, the input capacitance, the conductance of hyperpolarization-activated current, and the EPSC time course. In contrast to these gradients, the conductance of low-threshold K+ current and the expression of Kv1.2 channel protein were maximal in the central (middle-CF) region of NL. As a result, the middle-CF neuron had the smallest input resistance and membrane time constant, and consequently the fastest EPSP, and exhibited the most accurate coincidence detection. The specialization of middle-CF neurons as coincidence detectors may account for the high resolution of sound-source localization in the middle-frequency range observed in avians.
Figures


References
-
- Agmon-Snir H, Carr CE, Rinzel J (1998) The role of dendrites in auditory coincidence detection. Nature 393: 268-272. - PubMed
-
- Barnes-Davies M, Barker MC, Osmani F, Forsythe ID (2004) Kv1 currents mediate a gradient of principal neuron excitability across the tonotopic axis in the rat lateral superior olive. Eur J Neurosci 19: 325-333. - PubMed
-
- Brown TH, Fricke RA, Perkel DH (1981) Passive electrical constants in three classes of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 4: 812-827. - PubMed
-
- Bruckner S, Hyson RL (1998) Effect of GABA on the processing of interaural time differences in nucleus laminaris neurons in the chick. Eur J Neurosci 10: 3438-3450. - PubMed
-
- Carr CE, Boudreau RE (1993a) Organization of the nucleus magnocellularis and the nucleus laminaris in the barn owl: encoding and measuring interaural time differences. J Comp Neurol 334: 337-355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
