Parkin mediates nonclassical, proteasomal-independent ubiquitination of synphilin-1: implications for Lewy body formation
- PMID: 15728840
- PMCID: PMC6726069
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4474-04.2005
Parkin mediates nonclassical, proteasomal-independent ubiquitination of synphilin-1: implications for Lewy body formation
Abstract
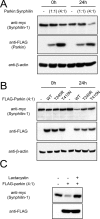
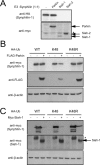
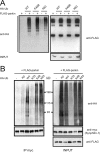
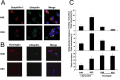
It is widely accepted that the familial Parkinson's disease (PD)-linked gene product, parkin, functions as a ubiquitin ligase involved in protein turnover via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Substrates ubiquitinated by parkin are hence thought to be destined for proteasomal degradation. Because we demonstrated previously that parkin interacts with and ubiquitinates synphilin-1, we initially expected synphilin-1 degradation to be enhanced in the presence of parkin. Contrary to our expectation, we found that synphilin-1 is normally ubiquitinated by parkin in a nonclassical, proteasomal-independent manner that involves lysine 63 (K63)-linked polyubiquitin chain formation. Parkin-mediated degradation of synphilin-1 occurs appreciably only at an unusually high parkin to synphilin-1 expression ratio or when primed for lysine 48 (K48)-linked ubiquitination. In addition we found that parkin-mediated ubiquitination of proteins within Lewy-body-like inclusions formed by the coexpression of synphilin-1, alpha-synuclein, and parkin occurs predominantly via K63 linkages and that the formation of these inclusions is enhanced by K63-linked ubiquitination. Our results suggest that parkin is a dual-function ubiquitin ligase and that K63-linked ubiquitination of synphilin-1 by parkin may be involved in the formation of Lewy body inclusions associated with PD.
Figures


References
-
- Ardley HC, Tan NG, Rose SA, Markham AF, Robinson PA (2001) Features of the parkin/ariadne-like ubiquitin ligase, HHARI, that regulate its interaction with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, Ubch7. J Biol Chem 276: 19640-19647. - PubMed
-
- Chau V, Tobias JW, Bachmair A, Marriott D, Ecker DJ, Gonda DK, Varshavsky A (1989) A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science 243: 1576-1583. - PubMed
-
- Choi P, Snyder H, Petrucelli L, Theisler C, Chong M, Zhang Y, Lim K, Chung KK, Kehoe K, D'Adamio L, Lee JM, Cochran E, Bowser R, Dawson TM, Wolozin B (2003) SEPT5_v2 is a parkin-binding protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 117: 179-189. - PubMed
-
- Chung KK, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2001a) The role of the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 24: S7-14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
