Biological characterization of novel inhibitors of the gram-positive DNA polymerase IIIC enzyme
- PMID: 15728893
- PMCID: PMC549236
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.3.987-995.2005
Biological characterization of novel inhibitors of the gram-positive DNA polymerase IIIC enzyme
Abstract
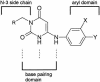
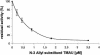
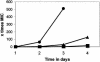
Novel N-3-alkylated 6-anilinouracils have been identified as potent and selective inhibitors of bacterial DNA polymerase IIIC, the enzyme essential for the replication of chromosomal DNA in gram-positive bacteria. A nonradioactive assay measuring the enzymatic activity of the DNA polymerase IIIC in gram-positive bacteria has been assembled. The 6-anilinouracils described inhibited the polymerase IIIC enzyme at concentrations in the nanomolar range in this assay and displayed good in vitro activity (according to their MICs) against staphylococci, streptococci, and enterococci. The MICs of the most potent derivatives were about 4 microg/ml for this panel of bacteria. The 50% effective dose of the best compound (6-[(3-ethyl-4-methylphenyl)amino]-3-{[1-(isoxazol-5-ylcarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]methyl}uracil) was 10 mg/kg of body weight after intravenous application in a staphylococcal sepsis model in mice, from which in vivo pharmacokinetic data were also acquired.
Figures
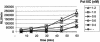


References
-
- Ali, A., S. D. Aster, D. W. Graham, G. F. Patel, G. E. Taylor, R. L. Tolman, R. E. Painter, L. L. Silver, K. Young, K. Ellsworth, W. Geissler, and G. S. Harris. 2001. Design and synthesis of novel antimicrobial agents with inhibitory activity against DNA polymerase III. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11:2185-2188. - PubMed
-
- Ali, A., G. E. Taylor, K. Ellsworth, G. Harris, R. Painter, L. L. Silver, and K. Young. 2003. Novel pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-based inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus DNA polymerase III: design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 46:1824-1830. - PubMed
-
- Ali, A., G. E. Taylor and D. W. Graham. April. 2001. Gram-positive selective antibacterial compounds, compositions containing such compounds and methods of treatment. Patent WO 01/29010.
-
- Barnes, M. H., R. A. Hammond, C. C. Kennedy, S. L. Mack, and N. C. Brown. 1992. Localization of the exonuclease and polymerase domains of Bacillus subtilis DNA polymerase III. Gene 111:43-49. - PubMed
-
- Bhamidipati, R. K., P. V. Dravid, R. Mullangi, and N. R. Srinivas. 2004. Prediction of clinical pharmacokinetic parameters of linezolid using animal data by allometric scaling: applicability for the development of novel oxazolidinones. Xenobiotica 34:571-579. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

