Rat/MgrA, a regulator of autolysis, is a regulator of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 15731040
- PMCID: PMC1064946
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1423-1431.2005
Rat/MgrA, a regulator of autolysis, is a regulator of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
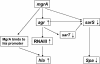
We have previously identified mgrA (rat) as a regulator of autolysis in Staphylococcus aureus. Besides its effect on autolytic activity, we recently found alterations in the expression of regulator and target virulence genes in the mgrA mutant. Northern analysis and transcription fusion assays showed that inactivation of mgrA has led to the downregulation of RNAIII of agr and hla and upregulation of sarS and spa. Although both SarA and agr are activators of alpha-hemolysin and a repressors of protein A synthesis, we found that the transcription of sarA was not affected in the mgrA mutant and vice versa, indicating that MgrA likely regulates hla and spa in a SarA-independent manner. Previously we have shown that SarT, a SarA homolog, is a repressor of hla and an activator of spa, presumably by activating SarS, however, analysis of the double sarT mgrA mutant for hla and spa transcription indicated that the mgrA-mediated effect is not mediated via sarT. Our results further demonstrated that the mgrA gene product regulates hla and spa expression in a dual fashion, with the first being agr dependent and the second agr independent. In the agr-independent pathway, MgrA binds directly to hla and the sarS promoter to modulate alpha-hemolysin and protein A expression. Thus, our studies here have defined the nature of interaction of mgrA with other regulators such as agr, sarS, and sarT and its role in regulating hla and spa transcription within the virulence regulatory network of S. aureus.
Figures
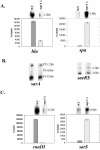

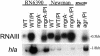
 , agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191. B. Northern blot analysis of the hla transcript in RN6390 and isogenic mutants. The probe for hla was an 800-bp fragment encompassing the open reading frame. RNA was harvested from cells grown to an OD650 of ≈1.2, representing late exponential phase. The expression of GFP driven by the hla promoter was also measured. Promoter activation was plotted as mean fluorescence/OD650 ratio, using average values of triplicate readings at an OD650 of ≈1.4. This experiment was repeated at least three times with similar results. ▧, RN6390; ░⃞, mgrA mutant ALC2530; ▥, sarT mutant ALC3043; ▩, agr mutant RN6911; ▤, sarT mgrA mutant ALC3046;
, agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191. B. Northern blot analysis of the hla transcript in RN6390 and isogenic mutants. The probe for hla was an 800-bp fragment encompassing the open reading frame. RNA was harvested from cells grown to an OD650 of ≈1.2, representing late exponential phase. The expression of GFP driven by the hla promoter was also measured. Promoter activation was plotted as mean fluorescence/OD650 ratio, using average values of triplicate readings at an OD650 of ≈1.4. This experiment was repeated at least three times with similar results. ▧, RN6390; ░⃞, mgrA mutant ALC2530; ▥, sarT mutant ALC3043; ▩, agr mutant RN6911; ▤, sarT mgrA mutant ALC3046;  , agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191.
, agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191.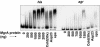

 , agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191.
, agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191.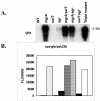
 , agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191.
, agr mgrA mutant ALC2537; ▪ agr sarT mutant ALC3188; and □ mgrA sarT agr mutant ALC3191.

Similar articles
-
Regulatory role of proteins binding to the spa (protein A) and sarS (staphylococcal accessory regulator) promoter regions in Staphylococcus aureus NTCC 8325-4.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Aug;295(4):253-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.05.003. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16128400
-
Identification of sarV (SA2062), a new transcriptional regulator, is repressed by SarA and MgrA (SA0641) and involved in the regulation of autolysis in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(16):5267-80. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.16.5267-5280.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15292128 Free PMC article.
-
SarT influences sarS expression in Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 2003 Sep;71(9):5139-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5139-5148.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12933857 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 Apr 5;7(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0031-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0031-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 30953424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An insight into pleiotropic regulators Agr and Sar: molecular probes paving the new way for antivirulent therapy.Future Microbiol. 2013 Oct;8(10):1339-53. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.92. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24059923 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Reveals the Effect of a MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AHA_2124 on Aeromonas hydrophila.Biology (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;12(12):1473. doi: 10.3390/biology12121473. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132299 Free PMC article.
-
A Functional ClpXP Protease is Required for Induction of the Accessory Toxin Genes, tst, sed, and sec.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 28;12(9):553. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090553. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872362 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence strategies of the dominant USA300 lineage of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA).FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012 Jun;65(1):5-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.00937.x. Epub 2012 Mar 5. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22309135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional profiling of XdrA, a new regulator of spa transcription in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):5151-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00491-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20675497 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of the meat starter culture bacterium Staphylococcus carnosus TM300.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Feb;75(3):811-22. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01982-08. Epub 2008 Dec 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19060169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvidson, S., and K. Tegmark. 2001. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 291:159-170. - PubMed
-
- Chang, S., D. M. Sievert, J. C. Hageman, et al. 2003. Infection with vancomycin-resistance S. aureus containing vanA resistance gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1342-1347. - PubMed
-
- Cheung, A. L., A. S. Bayer, G. Zhang, H. Gresham, and Y.-Q. Xiong. 2004. Regulation of virulence determinants in vitro and in vivo in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1649:1-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

