Biofilm formation, icaADBC transcription, and polysaccharide intercellular adhesin synthesis by staphylococci in a device-related infection model
- PMID: 15731082
- PMCID: PMC1064907
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1811-1819.2005
Biofilm formation, icaADBC transcription, and polysaccharide intercellular adhesin synthesis by staphylococci in a device-related infection model
Abstract
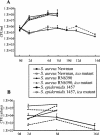
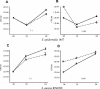
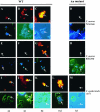
Biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus is mediated by the polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) encoded by the ica operon. We used a device-related animal model to investigate biofilm formation, PIA expression (immunofluorescence), and ica transcription (quantitative transcript analysis) throughout the course of infection by using two prototypic S. aureus strains and one S. epidermidis strain as well as corresponding ica mutants. During infection, the ica mutants were growth attenuated when inoculated in competition with the corresponding wild-type strains but not when grown singly. A typical biofilm was observed at the late course of infection. Only in S. aureus RN6390, not in S. aureus Newman, were PIA and ica-specific transcripts detectable after anaerobic growth in vitro. However, both S. aureus strains were PIA positive in vivo by day 8 of infection. ica transcription preceded PIA expression and biofilm formation in vivo. In S. epidermidis, both PIA and ica expression levels were elevated compared to those in the S. aureus strains in vitro as well as in vivo and were detectable throughout the course of infection. In conclusion, in S. aureus, PIA expression is dependent on the genetic background of the strain as well as on strong inducing conditions, such as those dominating in vivo. In S. epidermidis, PIA expression is elevated and less vulnerable to environmental conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Christensen, G. D., W. A. Simpson, J. J. Younger, L. M. Baddour, F. F. Barrett, D. M. Melton, and E. H. Beachey. 1985. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 22:996-1006. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

