Systematic pathogenesis and replication of avian hepatitis E virus in specific-pathogen-free adult chickens
- PMID: 15731237
- PMCID: PMC1075698
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3429-3437.2005
Systematic pathogenesis and replication of avian hepatitis E virus in specific-pathogen-free adult chickens
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(13):6721
Abstract
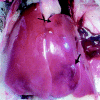
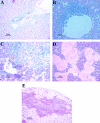
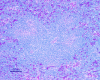
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is an important human pathogen. Due to the lack of a cell culture system and a practical animal model for HEV, little is known about its pathogenesis and replication. The discovery of a strain of HEV in chickens, designated avian HEV, prompted us to evaluate chickens as a model for the study of HEV. Eighty-five 60-week-old specific-pathogen-free chickens were randomly divided into three groups. Group 1 chickens (n=28) were each inoculated with 5 x 10(4.5) 50% chicken infectious doses of avian HEV by the oronasal route, group 2 chickens (n=29) were each inoculated with the same dose by the intravenous (i.v.) route, and group 3 chickens (n=28) were not inoculated and were used as controls. Two chickens from each group were necropsied at 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 13, 16, 20, 24, 28, 35, and 42 days postinoculation (dpi), and the remaining chickens were necropsied at 56 dpi. Serum, fecal, and various tissue samples, including liver and spleen samples, were collected at each necropsy for pathological and virological testing. By 21 dpi, all oronasally and i.v. inoculated chickens had seroconverted. Fecal virus shedding was detected variably from 1 to 20 dpi for the i.v. group and from 10 to 56 dpi for the oronasal group. Avian HEV RNA was detected in serum, bile, and liver samples from both i.v. and oronasally inoculated chickens. Gross liver lesions, characterized by subcapsular hemorrhages or enlargement of the right intermediate lobe, were observed in 7 of 28 oronasally and 7 of 29 i.v. inoculated chickens. Microscopic liver lesions were mainly lymphocytic periphlebitis and phlebitis. The lesion scores were higher for oronasal (P=0.0008) and i.v. (P=0.0029) group birds than for control birds. Slight elevations of the plasma liver enzyme lactate dehydrogenase were observed in infected chickens. The results indicated that chickens are a useful model for studying HEV replication and pathogenesis. This is the first report of HEV transmission via its natural route in a homologous animal model.
Figures


References
-
- Aggarwal, R., and K. Krawczynski. 2000. Hepatitis E: an overview and recent advances in clinical and laboratory research. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15:9-20. - PubMed
-
- Arankalle, V. A., M. K. Goverdhan, and K. Banerjee. 1994. Antibodies against hepatitis E virus in Old World monkeys. J. Viral Hepat. 1:125-129. - PubMed
-
- Balayan, M. S., A. G. Andjaparidze, S. S. Savinskaya, E. S. Ketiladze, D. M. Braginsky, A. P. Savinov, and V. F. Poleschuk. 1983. Evidence for a virus in non-A, non-B hepatitis transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Intervirology 20:23-31. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, D. W., K. Krawczynski, E. H. Cook, Jr., K. A. McCaustland, C. D. Humphrey, J. E. Spelbring, H. Myint, and J. E. Maynard. 1987. Enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis: serial passage of disease in cynomolgus macaques and tamarins and recovery of disease-associated 27- to 34-nm viruslike particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:6277-6281. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

