Markers of inflammation are negatively correlated with serum leptin in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15731289
- PMCID: PMC1755600
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.032243
Markers of inflammation are negatively correlated with serum leptin in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Leptin regulates food intake and modulates immunity and inflammation. A positive feedback mechanism has been described between tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and leptin, and it has been suggested that leptin potentiates inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objective: To assess whether inflammation correlates with leptin concentrations in patients with RA, and whether anti-TNF treatment modulates leptin concentrations in these patients.
Methods: Leptin, IL6 and CRP were measured (at baseline and after 2 weeks of treatment) in the blood of 31 patients with RA starting either anti-TNF treatment or placebo, and in 18 healthy controls.
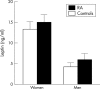
Results: In patients with RA, plasma leptin concentrations at baseline correlated inversely with the degree of inflammation as assessed by C reactive protein (CRP; r(s)(2) = 0.21, p<0.01) or interleukin (IL) 6 concentrations (r(s)(2) = 0.22, p<0.008). Mean (SD) leptin concentrations did not differ between patients with RA and controls (6.0 (4.6) v 4.2 (2.8) ng/ml in men; 15.1 (7.9) v 13.4 (5.2) ng/ml in women). Short course anti-TNF treatment for 2 weeks did not modify leptin concentrations, despite significant reduction of CRP and IL6.
Conclusion: A significant inverse correlation between inflammation and leptin concentrations was found in patients with active RA, although plasma leptin concentrations did not significantly differ from those in healthy controls. This suggests that active chronic inflammation may lower plasma leptin concentrations. Two weeks' treatment with anti-TNF did not change plasma leptin concentrations and longer treatment may be needed to see an effect on leptin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Feb;64(2):303-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.023119. Epub 2004 Jul 1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15231512 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Circulating leptin and adiponectin concentrations during tumor necrosis factor blockade in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2009 Apr;36(4):724-30. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.080626. Epub 2009 Feb 27. J Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19273452
-
Anti-TNF-alpha therapy does not modulate leptin in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009 Mar-Apr;27(2):222-8. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19473561
-
[New drugs and treatment strategies for rheumatoid arthritis].Recenti Prog Med. 2003 Sep;94(9):361-79. Recenti Prog Med. 2003. PMID: 12942798 Review. Italian.
-
Down-titration and discontinuation strategies of tumour necrosis factor-blocking agents for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with low disease activity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 24;5(5):CD010455. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010455.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31125448 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Adipocytokines as driving forces in rheumatoid arthritis].Z Rheumatol. 2007 Mar;66(2):139-41. doi: 10.1007/s00393-007-0158-4. Z Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17333076 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
Metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:710928. doi: 10.1155/2013/710928. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23431244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides and their receptors in the osteoarticular system: from basic to translational research.Endocr Rev. 2012 Aug;33(4):623-51. doi: 10.1210/er.2011-1016. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Endocr Rev. 2012. PMID: 22736674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal influences between leptin and glucocorticoids during acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2013 Oct;202(5):339-52. doi: 10.1007/s00430-013-0294-1. Epub 2013 May 16. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23677171
-
Adiponectin and leptin serum concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2010 Apr;30(6):731-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-009-1053-x. Epub 2009 Jul 12. Rheumatol Int. 2010. PMID: 19597733
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

