Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis
- PMID: 15731292
- PMCID: PMC1755629
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.025270
Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: To compare selected immunohistological features of inflammation in synovial tissue from patients with early and late osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods: Synovial tissue samples were obtained from 10 patients with knee pain, normal radiographs, and arthroscopic manifestations of OA (early OA), and from 15 patients with OA undergoing knee joint arthroplasty (late OA). Conventional immunohistochemical techniques were used to measure microscopic manifestations of inflammation. The inflammatory cell infiltrate, blood vessel formation, and angiogenic factors, NF-kappaB activation, expression of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) and interleukin 1beta (IL1beta), and the presence of cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 were quantified. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were isolated from early and late OA tissue samples to compare in vitro production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
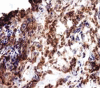
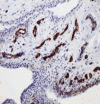
Results: Synovial tissue from patients with early OA demonstrated significantly greater CD4+ (p = 0.017) and CD68+ (p<0.001) cell infiltration, blood vessel formation (p = 0.01), vascular endothelial growth factor (p = 0.001), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression (p<0.001). Numbers of cells producing TNFalpha and IL1beta were also significantly greater in early OA (p<0.001). Manifestations of inflammation in early OA were associated with increased expression of the NF-kappaB1 (p<0.001) and RelA (p = 0.015) subunits, and with increased COX-2 expression (p = 0.04). Cytokine-induced PGE2 production by cultured FLS was similar in both groups.
Conclusion: Increased mononuclear cell infiltration and overexpression of mediators of inflammation were seen in early OA, compared with late OA. Isolated FLS were functionally similar in both groups, consistent with microenvironmental differences in the synovial tissue during different phases of OA. These observations may have important therapeutic implications for some patients during the early evolution of OA.
Figures
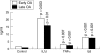
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

