Evolutionarily conserved human targets of adenosine to inosine RNA editing
- PMID: 15731336
- PMCID: PMC549564
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki239
Evolutionarily conserved human targets of adenosine to inosine RNA editing
Abstract
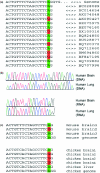
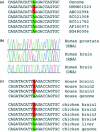
A-to-I RNA editing by ADARs is a post-transcriptional mechanism for expanding the proteomic repertoire. Genetic recoding by editing was so far observed for only a few mammalian RNAs that are predominantly expressed in nervous tissues. However, as these editing targets fail to explain the broad and severe phenotypes of ADAR1 knockout mice, additional targets for editing by ADARs were always expected. Using comparative genomics and expressed sequence analysis, we identified and experimentally verified four additional candidate human substrates for ADAR-mediated editing: FLNA, BLCAP, CYFIP2 and IGFBP7. Additionally, editing of three of these substrates was verified in the mouse while two of them were validated in chicken. Interestingly, none of these substrates encodes a receptor protein but two of them are strongly expressed in the CNS and seem important for proper nervous system function. The editing pattern observed suggests that some of the affected proteins might have altered physiological properties leaving the possibility that they can be related to the phenotypes of ADAR1 knockout mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Determination of editors at the novel A-to-I editing positions.Neurosci Res. 2008 Jun;61(2):201-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2008.02.009. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18407364
-
RNA editing by mammalian ADARs.Adv Genet. 2011;73:87-120. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380860-8.00003-3. Adv Genet. 2011. PMID: 21310295 Review.
-
Comparative genomic and bioinformatic approaches for the identification of new adenosine-to-inosine substrates.Methods Enzymol. 2007;424:245-64. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)24011-X. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17662844
-
Vaccinia virus E3L interferon resistance protein inhibits the interferon-induced adenosine deaminase A-to-I editing activity.Virology. 2001 Oct 25;289(2):378-87. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1154. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11689059
-
A-to-I editing challenger or ally to the microRNA process.Biochimie. 2007 Oct;89(10):1171-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jun 8. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 17628290 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of human RNA editing sites: A historical perspective.Methods. 2016 Sep 1;107:42-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 May 18. Methods. 2016. PMID: 27208508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Letter from the editor: Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing in Alu repeats in the human genome.EMBO Rep. 2005 Sep;6(9):831-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400507. EMBO Rep. 2005. PMID: 16138094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Explaining Pathogenicity of Congenital Zika and Guillain-Barré Syndromes: Does Dysregulation of RNA Editing Play a Role?Bioessays. 2019 Jun;41(6):e1800239. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800239. Epub 2019 May 20. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 31106880 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale mRNA sequencing determines global regulation of RNA editing during brain development.Genome Res. 2009 Jun;19(6):978-86. doi: 10.1101/gr.089409.108. Epub 2009 May 6. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19420382 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I RNA editing - immune protector and transcriptome diversifier.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Aug;19(8):473-490. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0006-1. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29692414 Review.
References
-
- Polson A.G., Crain P.F., Pomerantz S.C., McCloskey J.A., Bass B.L. The mechanism of adenosine to inosine conversion by the double-stranded RNA unwinding/modifying activity: a high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Biochemistry. 1991;30:11507–11514. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q., Khillan J., Gadue P., Nishikura K. Requirement of the RNA editing deaminase ADAR1 gene for embryonic erythropoiesis. Science. 2000;290:1765–1768. - PubMed
-
- Palladino M.J., Keegan L.P., O'Connell M.A., Reenan R.A. A-to-I pre-mRNA editing in Drosophila is primarily involved in adult nervous system function and integrity. Cell. 2000;102:437–449. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi M., Maas S., Single F.N., Hartner J., Rozov A., Burnashev N., Feldmeyer D., Sprengel R., Seeburg P.H. Point mutation in an AMPA receptor gene rescues lethality in mice deficient in the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR2. Nature. 2000;406:78–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

