Target-dependent on/off switch increases ribozyme fidelity
- PMID: 15731344
- PMCID: PMC549572
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki278
Target-dependent on/off switch increases ribozyme fidelity
Abstract
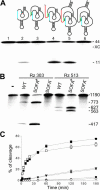
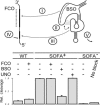
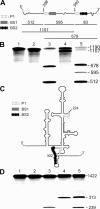
Ribozymes, RNA molecules that catalyze the cleavage of RNA substrates, provide an interesting alternative to the RNA interference (RNAi) approach to gene inactivation, especially given the fact that RNAi seems to trigger an immunological response. Unfortunately, the limited substrate specificity of ribozymes is considered to be a significant hurdle in their development as molecular tools. Here, we report the molecular engineering of a ribozyme possessing a new biosensor module that switches the cleavage activity from 'off' (a 'safety lock') to 'on' solely in the presence of the appropriate RNA target substrate. Both proof-of-concept and the mechanism of action of this man-made riboswitch are demonstrated using hepatitis delta virus ribozymes that cleave RNA transcripts derived from the hepatitis B and C viruses. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a ribozyme bearing a target-dependent module that is activated by its RNA substrate, an arrangement which greatly diminishes non-specific effects. This new approach provides a highly specific and improved tool with significant potential for application in the fields of both functional genomics and gene therapy.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of the SOFA delta ribozyme.RNA. 2005 Dec;11(12):1858-68. doi: 10.1261/rna.2112705. Epub 2005 Oct 26. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16251383 Free PMC article.
-
Development of ribozyme-based gene-inactivations; the example of the hepatitis delta virus ribozyme.Curr Gene Ther. 2007 Jun;7(3):205-16. doi: 10.2174/156652307780859008. Curr Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17584038 Review.
-
Target-induced SOFA-HDV ribozyme.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;848:369-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-545-9_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22315081
-
Ribozymes of the hepatitis delta virus: recent findings on their structure, mechanism of catalysis and possible applications.Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(2):409-18. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001. PMID: 11732611 Review.
-
Ribozyme-based gene-inactivation systems require a fine comprehension of their substrate specificities; the case of delta ribozyme.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Dec;10(23):2589-97. doi: 10.2174/0929867033456486. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14529473 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of the SOFA delta ribozyme.RNA. 2005 Dec;11(12):1858-68. doi: 10.1261/rna.2112705. Epub 2005 Oct 26. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16251383 Free PMC article.
-
A modern mode of activation for nucleic acid enzymes.PLoS One. 2007 Jul 25;2(7):e673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000673. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17653287 Free PMC article.
-
A Conserved Target Site in HIV-1 Gag RNA is Accessible to Inhibition by Both an HDV Ribozyme and a Short Hairpin RNA.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014 Jul 29;3(7):e178. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2014.31. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014. PMID: 25072692 Free PMC article.
-
Programming anti-ribozymes to sense trigger RNAs for modulating gene expression in mammalian cells.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 8;10(3):827-834. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.03.011. eCollection 2025 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40291978 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating a new generation of ribozymes in order to target HCV.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 10;5(3):e9627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009627. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20224783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewin A.S., Hauswirth W.W. Ribozyme gene therapy: applications for molecular medicine. Trends Mol. Med. 2001;7:221–228. - PubMed
-
- Michienzi A., Rossi J.J. Intracellular applications of ribozymes. Methods Enzymol. 2001;341:581–596. - PubMed
-
- Pebernard S., Iggo R.D. Determinants of interferon-stimulated gene induction by RNAi vectors. Differentiation. 2004;72:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Carlson C.B., Stephens O.M., Beal P.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA by proteins and small molecules. Biopolymers. 2003;70:86–102. - PubMed
-
- Sledz C.A., Holko M., de Veer M.J., Silverman R.H., Williams B.R. Activation of the interferon system by short-interfering RNAs. Nature Cell Biol. 2003;5:834–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

