ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
- PMID: 15731348
- PMCID: PMC553328
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409773102
ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
Abstract
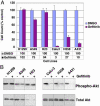
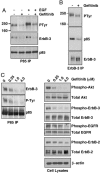
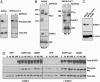
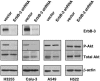
Therapies that target the EGF receptor (EGFR), such as gefitinib (IRESSA), are effective in a subset of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The differences in intracellular signaling networks between gefitinib-sensitive and -resistant NSCLCs remain poorly understood. In this study, we observe that gefitinib reduces phospho-Akt levels only in NSCLC cell lines in which it inhibits growth. To elucidate the mechanism underlying this observation, we compared immunoprecipitates of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) between gefitinib-sensitive and -resistant NSCLC cell lines. We observe that PI3K associates with ErbB-3 exclusively in gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines. Gefitinib dissociates this complex, thereby linking EGFR inhibition to decreased Akt activity. In contrast, gefitinib-resistant cells do not use ErbB-3 to activate the PI3K/Akt pathway. In fact, abundant ErbB-3 expression is detected only in gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines. Two gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines with endogenous distinct activating EGFR mutations (L858R and Del747-749), frequently observed in NSCLC patients who respond to gefitinib, also use ErbB-3 to couple to PI3K. Down-regulation of ErbB-3 by means of short hairpin RNA leads to decreased phospho-Akt levels in the gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines, Calu-3 (WT EGFR) and H3255 (L858R EGFR), but has no effect on Akt activation in the gefitinib-resistant cell lines, A549 and H522. We conclude that ErbB-3 is used to couple EGFR to the PI3K/Akt pathway in gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines harboring WT and mutant EGFRs.
Figures
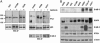
References
-
- Breathnach, O. S., Freidlin, B., Conley, B., Green, M. R., Johnson, D. H., Gandara, D. R., O'Connell, M., Shepherd, F. A. & Johnson, B. E. (2001) J. Clin. Oncol. 19, 1734-1742. - PubMed
-
- Schiller, J. H., Harrington, D., Belani, C. P., Langer, C., Sandler, A., Krook, J., Zhu, J. & Johnson, D. H. (2002) N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 92-98. - PubMed
-
- Laskin, J. J. & Sandler, A. B. (2004) Cancer Treat. Rev. 30, 1-17. - PubMed
-
- Riese, D. J., II, & Stern, D. F. (1998) Bioessays 20, 41-48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

