Regulation of ryanodine receptors by calsequestrin: effect of high luminal Ca2+ and phosphorylation
- PMID: 15731387
- PMCID: PMC1305491
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.051441
Regulation of ryanodine receptors by calsequestrin: effect of high luminal Ca2+ and phosphorylation
Abstract
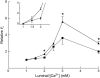
Calsequestrin, the major calcium sequestering protein in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle, forms a quaternary complex with the ryanodine receptor calcium release channel and the intrinsic membrane proteins triadin and junctin. We have investigated the possibility that calsequestrin is a luminal calcium concentration sensor for the ryanodine receptor. We measured the luminal calcium concentration at which calsequestrin dissociates from the ryanodine receptor and the effect of calsequestrin on the response of the ryanodine receptor to changes in luminal calcium. We provide electrophysiological and biochemical evidence that: 1), luminal calcium concentration of >/=4 mM dissociates calsequestrin from junctional face membrane, whereas in the range of 1-3 mM calsequestrin remains attached; 2), the association with calsequestrin inhibits ryanodine receptor activity, but amplifies its response to changes in luminal calcium concentration; and 3), under physiological calcium conditions (1 mM), phosphorylation of calsequestrin does not alter its ability to inhibit native ryanodine receptor activity when the anchoring proteins triadin and junctin are present. These data suggest that the quaternary complex is intact in vivo, and provides further evidence that calsequestrin is involved in the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium signaling pathway and has a role as a luminal calcium sensor for the ryanodine receptor.
Figures




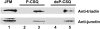
References
-
- Ahern, G. P., P. R. Junankar, and A. F. Dulhunty. 1994. Single channel activity of the ryanodine receptor calcium release channel is modulated by FK-506. FEBS Lett. 352:369–374. - PubMed
-
- Beard, N. A. 2003. Regulation of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor by calsequestrin. PhD thesis. Australian National University, Canberra, Australia.
-
- Beard, N. A., D. R. Laver, and A. F. Dulhunty. 2004. Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 155:33–69. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, N. R., A. H. Caswell, S. R. Wen, and J. A. Talvenheimo. 1990. Molecular interactions of the junctional foot protein and dihydropyridine receptor in skeletal muscle triads. J. Membr. Biol. 113:237–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

