Proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15734904
- PMCID: PMC1065393
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.058719
Proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis
Abstract
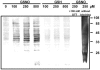
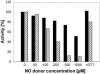
Although nitric oxide (NO) has grown into a key signaling molecule in plants during the last few years, less is known about how NO regulates different events in plants. Analyses of NO-dependent processes in animal systems have demonstrated protein S-nitrosylation of cysteine (Cys) residues to be one of the dominant regulation mechanisms for many animal proteins. For plants, the principle of S-nitrosylation remained to be elucidated. We generated S-nitrosothiols by treating extracts from Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) cell suspension cultures with the NO-donor S-nitrosoglutathione. Furthermore, Arabidopsis plants were treated with gaseous NO to analyze whether S-nitrosylation can occur in the specific redox environment of a plant cell in vivo. S-Nitrosylated proteins were detected by a biotin switch method, converting S-nitrosylated Cys to biotinylated Cys. Biotin-labeled proteins were purified and analyzed using nano liquid chromatography in combination with mass spectrometry. We identified 63 proteins from cell cultures and 52 proteins from leaves that represent candidates for S-nitrosylation, including stress-related, redox-related, signaling/regulating, cytoskeleton, and metabolic proteins. Strikingly, many of these proteins have been identified previously as targets of S-nitrosylation in animals. At the enzymatic level, a case study demonstrated NO-dependent reversible inhibition of plant glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, suggesting that this enzyme could be affected by S-nitrosylation. The results of this work are the starting point for further investigation to get insight into signaling pathways and other cellular processes regulated by protein S-nitrosylation in plants.
Figures



Comment in
-
Protein S-nitrosylation: potential targets and roles in signal transduction.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jul;144(3):1237-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.900228. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17616506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Identification of endogenously S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis plantlets: effect of cold stress on cysteine nitrosylation level.Plant Sci. 2014 Feb;215-216:150-6. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.10.014. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24388526
-
Identification of nuclear target proteins for S-nitrosylation in pathogen-treated Arabidopsis thaliana cell cultures.Plant Sci. 2015 Sep;238:115-26. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.011. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26259180
-
Computational prediction of candidate proteins for S-nitrosylation in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 21;9(10):e110232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110232. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25333472 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in plants.Methods Enzymol. 2008;440:283-93. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)00818-X. Methods Enzymol. 2008. PMID: 18423225 Review.
-
Screening systems for the identification of S-nitrosylated proteins.Nitric Oxide. 2011 Aug 1;25(2):108-11. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Nitric Oxide. 2011. PMID: 21111056 Review.
Cited by
-
S-Nitrosoglutathione is a component of wound- and salicylic acid-induced systemic responses in Arabidopsis thaliana.J Exp Bot. 2012 May;63(8):3219-27. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers043. Epub 2012 Feb 27. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22371078 Free PMC article.
-
Current overview of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) in higher plants.Front Plant Sci. 2013 May 8;4:126. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00126. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23658557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
S-Adenosylmethionine Synthetase 3 Is Important for Pollen Tube Growth.Plant Physiol. 2016 Sep;172(1):244-53. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00774. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27482079 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein S-nitrosylation in plant growth and development.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Jul 30;43(8):204. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03290-z. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39080060 Review.
-
The Key Roles of ROS and RNS as a Signaling Molecule in Plant-Microbe Interactions.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 25;12(2):268. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020268. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aniya Y, Anders MW (1989) Activation of rat liver microsomal glutathione S-transferase by reduced oxygen species. J Biol Chem 264: 1998–2002 - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C (2001) Nitric oxide and the regulation of gene expression. Trends Cell Biol 11: 66–75 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 77: 248–254 - PubMed
-
- Carlberg I, Rintamaki E, Aro EM, Andersson B (1999) Thylakoid protein phosphorylation and the thiol redox state. Biochemistry 38: 3197–3204 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

