The links between axin and carcinogenesis
- PMID: 15735151
- PMCID: PMC1770611
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2003.009506
The links between axin and carcinogenesis
Erratum in
- J Clin Pathol. 2005 Dec;58(12):1344
Abstract
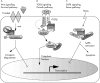
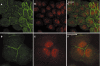
The products of the two mammalian Axin genes (Axin1 and its homologue Axin2) are essential for the degradation of beta catenin, a component of Wnt signalling that is frequently dysregulated in cancer cells. Axin is a multidomain scaffold protein that has many functions in biological signalling pathways. Overexpression of mutant [corrected] axin results in axis duplication in mouse embryos. Wnt signalling activity determines dorsal-ventral axis formation in vertebrates, implicating axin as a negative regulator of this signalling pathway. In addition, Wnts modulate pattern formation and the morphogenesis of most organs by influencing and controlling cell proliferation, motility, and fate. Defects in different components of the Wnt signalling pathway promote tumorigenesis and tumour progression. Recent biochemical studies of axins indicate that these molecules are the primary limiting components of this pathway. This review explores the intriguing connections between defects in axin function and human diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Zeng L, Fagotto F, Zhang T, et al. The mouse Fused locus encodes axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signalling pathway that regulates embryonic axis formation. Cell 1997;90:181–92. - PubMed
-
- Satoh S, Daigo Y, Furukawa Y, et al. AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1. Nat Genet 2000;24:245–50. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama T . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2000;11:273–82. - PubMed
-
- Wodarz A, Nusse R. Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 1998;14:59–88. - PubMed
-
- Bienz M, Clevers H. Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 2000;103:311–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
