Identification of viral genes essential for replication of murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 using signature-tagged mutagenesis
- PMID: 15738413
- PMCID: PMC553290
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404521102
Identification of viral genes essential for replication of murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 using signature-tagged mutagenesis
Abstract
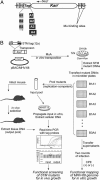
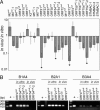
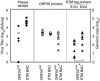
Gamma-herpesviruses, Epstein-Barr virus, and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus are important human pathogens, because they are involved in tumor development. Murine gamma-herpesvirus-68 (MHV-68 or gammaHV-68) has emerged as a small animal model system for the study of gamma-herpesvirus pathogenesis and host-virus interactions. To identify the genes required for viral replication in vitro and in vivo, we generated 1,152 mutants using signature-tagged transposon mutagenesis on an infectious bacterial artificial chromosome of MHV-68. Almost every ORF was mutated by random insertion. For each ORF, a mutant with an insertion proximal to the N terminus of each ORF was examined for the ability to grow in fibroblasts. Our results indicate that 41 genes are essential for in vitro growth, whereas 26 are nonessential and 6 attenuated. Replication-competent mutants were pooled to infect mice, which led to the discovery of ORF 54 being important for MHV-68 to replicate in the lung. This genetic analysis of a tumor-associated herpesvirus at the whole genome level validates signature-tagged transposon mutagenesis screening as an effective genetic system to identify important virulent genes in vivo and define interactions with the host immune system.
Figures

References
-
- Rickinson, A. B. & Kieff, E. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M. & Howley, P. M. (Lippincott William & Wilkins, Philadelphia), Vol. 2, pp. 2575-2627.
-
- Moore, P. S. & Chang, Y. (2001) in Fields Virology, eds. Knipe, D. M. & Howley, P. M. (Lippincott William & Wilkins, Philadelphia), Vol. 2, pp. 2803-2833.
-
- Simas, J. P. & Efstathiou, S. (1998) Trends Microbiol. 6, 276-282. - PubMed
-
- Virgin, H. W. & Speck, S. H. (1999) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 11, 371-379. - PubMed
-
- Speck, S. H. & Virgin, H. W. (1999) Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2, 403-409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

