Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas
- PMID: 15738415
- PMCID: PMC552785
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0500613102
Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas
Abstract
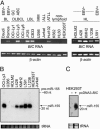
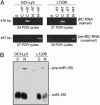
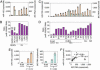
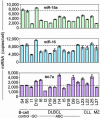
We show that the microRNA miR-155 can be processed from sequences present in BIC RNA, a spliced and polyadenylated but non-protein-coding RNA that accumulates in lymphoma cells. The precursor of miR-155 is likely a transient spliced or unspliced nuclear BIC transcript rather than accumulated BIC RNA, which is primarily cytoplasmic. By using a sensitive and quantitative assay, we find that clinical isolates of several types of B cell lymphomas, including diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), have 10- to 30-fold higher copy numbers of miR-155 than do normal circulating B cells. Similarly, the quantities of BIC RNA are elevated in lymphoma cells, but ratios of the amounts of the two RNAs are not constant, suggesting that the level of miR-155 is controlled by transcription and processing. Significantly higher levels of miR-155 are present in DLBCLs with an activated B cell phenotype than with the germinal center phenotype. Because patients with activated B cell-type DLBCL have a poorer clinical prognosis, quantification of this microRNA may be diagnostically useful.
Figures
References
-
- Haasch, D., Chen, Y. W., Reilly, R. M., Chiou, X. G., Koterski, S., Smith, M. L., Kroeger, P., McWeeny, K., Halbert, D. N., Mollison, K. W., et al. (2002) Cell. Immunol. 217, 78-86. - PubMed
-
- Metzler, M., Wilda, M., Busch, K., Viehmann, S. & Borkhardt, A. (2004) Genes Chromosomes Cancer 39, 167-169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

