Regulation of platelet granule exocytosis by S-nitrosylation
- PMID: 15738422
- PMCID: PMC553307
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408310102
Regulation of platelet granule exocytosis by S-nitrosylation
Abstract
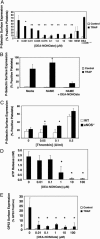
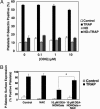
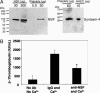
Nitric oxide (NO) regulates platelet activation by cGMP-dependent mechanisms and by mechanisms that are not completely defined. Platelet activation includes exocytosis of platelet granules, releasing mediators that regulate interactions between platelets, leukocytes, and endothelial cells. Exocytosis is mediated in part by N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF), an ATPase that disassembles complexes of soluble NSF attachment protein receptors. We now demonstrate that NO inhibits exocytosis of dense granules, lysosomal granules, and alpha-granules from human platelets by S-nitrosylation of NSF. Platelets lacking endothelial NO synthase show increased rolling on venules, increased thrombosis in arterioles, and increased exocytosis in vivo. Regulation of exocytosis is thus a mechanism by which NO regulates thrombosis.
Figures


References
-
- Moncada, S., Palmer, R. M. & Higgs, E. A. (1991) Pharmacol. Rev. 43, 109-142. - PubMed
-
- Loscalzo, J. (2001) Circ. Res. 88, 756-762. - PubMed
-
- Cirino, G., Fiorucci, S. & Sessa, W. C. (2003) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 91-95. - PubMed
-
- Radomski, M. W., Palmer, R. M. & Moncada, S. (1987) Lancet 2, 1057-1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL 074945/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 63706/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL065608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL 56091/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL056091/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 RR007002/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR 07002/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 074061/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074061/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063706/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL074945/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL 65608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

