Stereotactic IMRT for prostate cancer: dosimetric impact of multileaf collimator leaf width in the treatment of prostate cancer with IMRT
- PMID: 15738911
- PMCID: PMC5723465
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v5i2.1989
Stereotactic IMRT for prostate cancer: dosimetric impact of multileaf collimator leaf width in the treatment of prostate cancer with IMRT
Abstract
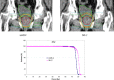
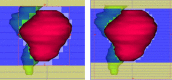
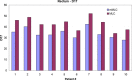
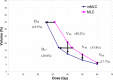
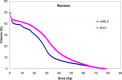
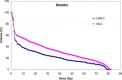
The focus of this work is the dosimetric impact of multileaf collimator (MLC) leaf width on the treatment of prostate cancer with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). Ten patients with prostate cancer were planned for IMRT delivery using two different MLC leaf widths--4mm and 10mm--representing the Radionics micro-multileaf collimator (mMLC) and Siemens MLC, respectively. Treatment planning was performed on the XKnifeRT2 treatment-planning system (Radionics, Burlington, MA). All beams and optimization parameters were identical for the mMLC and MLC plans. All the plans were normalized to ensure that 95% of the planning target volume (PTV) received 100% of the prescribed dose. The differences in dose distribution between the two different plans were assessed by dose-volume histogram (DVH) analysis of the target and critical organs. We specifically compared the volume of rectum receiving 40 Gy (V40), 50 Gy (V50), 60 Gy (V60), the dose received by 17% and 35% of rectum (D17 and D35), and the maximum dose to 1 cm3 of the rectum for a prescription dose of 74 Gy. For the urinary bladder, the dose received by 25% of bladder (D25), V40, and the maximum dose to 1 cm3 of the organ were recorded. For PTV we compared the maximum dose to the "hottest" 1 cm3 (Dmax1 cm3) and the dose to 99% of the PTV (D99). The dose inhomogeneity in the target, defined as the ratio of the difference in Dmax1 cm3 and D99 to the prescribed dose, was also compared between the two plans. In all cases studied, significant reductions in the volume of rectum receiving doses less than 65 Gy were seen using the mMLC. The average decrease in the volume of the rectum receiving 40 Gy, 50 Gy, and 60 Gy using the mMLC plans was 40.2%, 33.4%, and 17.7%, respectively, with p < 0.0001 for V40 and V50 and p < 0.012 for V60. The mean dose reductions for D17 and D35 for the rectum using the mMLC were 20.4% (p < 0.0001) and 18.3% (p < 0.0002), respectively. There were consistent reductions in all dose indices studied for the bladder. The target dose inhomogeneity was improved in the mMLC plans by an average of 29%. In the high-dose range, there was no significant difference in the dose deposited in the "hottest" 1 cm3 of the rectum between the two plans for all cases (p > 0.78). In conclusion, the use of the mMLC for IMRT of the prostate resulted in significant improvement in the DVH parameters of the prostate and critical organs, which may improve the therapeutic ratio.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dosimetric advantage and clinical implication of a micro-multileaf collimator in the treatment of prostate with intensity-modulated radiotherapy.Med Dosim. 2005 Summer;30(2):97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.03.002. Med Dosim. 2005. PMID: 15922176
-
Dosimetric study using different leaf-width MLCs for treatment planning of dynamic conformal arcs and intensity-modulated radiosurgery.Med Phys. 2005 Feb;32(2):405-11. doi: 10.1118/1.1842911. Med Phys. 2005. PMID: 15789586
-
Comparison of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and forward-planning dynamic arc therapy techniques for prostate cancer.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008 Oct 24;9(4):37-56. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v9i4.2783. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 19020481 Free PMC article.
-
[Intensity modulated radiotherapy with dynamic multileaf collimator. Technique and clinical experience].Cancer Radiother. 1999 Sep-Oct;3(5):378-92. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(00)87976-7. Cancer Radiother. 1999. PMID: 10572508 Review. French.
-
IMRT for prostate cancer: defining target volume based on correlated pathologic volume of disease.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 May 1;56(1):184-91. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00085-3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 12694837 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of multileaf collimator leaf width on the radiosurgery planning for spine lesion treatment in terms of the modulated techniques and target complexity.Radiat Oncol. 2014 Mar 8;9:72. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-9-72. Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24606890 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of MR-guided adaptive IMRT versus 3DOF-VMAT for prostate stereotactic radiotherapy.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2022 Mar 2;21:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2022.02.003. eCollection 2022 Mar. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35252598 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical commissioning and use of the Novalis Tx linear accelerator for SRS and SBRT.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2012 May 10;13(3):3729. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v13i3.3729. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22584170 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric impact of multileaf collimator leaf width according to sophisticated grade of technique in the IMRT and VMAT planning for pituitary adenoma lesion.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):78119-78126. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12974. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27806336 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric verification of micro-MLC based intensity modulated radiation therapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008 Jun 23;9(3):109-121. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v9i3.2832. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 18716597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LoSasso T, Chui CS, Kutcher GJ, Leibel SA, Fuks Z, Ling CC. The use of a multi‐leaf collimator for conformal radiotherapy of carcinomas of the prostate and nasopharynx. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1993;25:161–170. - PubMed
-
- Powlis WD, Smith AR, Cheng E et al. Initiation of multi‐leaf collimator conformal radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1993; 25:171–179. - PubMed
-
- Galvin JM, Smith AR, Lally B. Characterization of a multi‐leaf collimator system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1993;25:181–192. - PubMed
-
- Schlegel W, Pastyr O, Bortfeld T et al. Computer systems and mechanical tools for stereotactically guided conformation therapy with linear accelerators. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1992;24:781–787. - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove VP, Jahn U, Pfaender M, Bauer S, Budach V, Wurm RE. Commissioning of a micro multi‐leaf collimator and planning system for stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol 1999;50:325–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

