Age and manifestation related symptoms in familial adenomatous polyposis
- PMID: 15740631
- PMCID: PMC1079798
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-24
Age and manifestation related symptoms in familial adenomatous polyposis
Abstract
Background: To identify early symptoms of familial adenomatous polyposis with a view to improve early diagnosis and treatment. Diagnosis on the basis of genetic testing is usually limited to where there is a known family history, so FAP is more usually diagnosed on clinical grounds. Except for those identified via FAP registers, the majority of patients are symptomatic at the time of diagnosis.
Methods: We undertook a retrospective study of 143 FAP patients treated at the Department of Surgery, University of Erlangen between 1971 and 2000. We identified patterns of symptoms, endoscopic findings and extracolonic manifestations in three age groups.
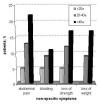
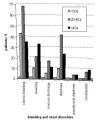
Results: FAP was diagnosed clinically on the basis of symptoms in 84% (120/143) of these patients. Most presented with intestinal symptoms such as colonic bleeding (68%) and diarrhea (42%). All but one of the patients between 20 and 40 years old had rectal polyps (98.7%, 75/76), whereas in those over 40 years old the prevalence was 76% (35/46). Non-specific symptoms such as abdominal pain, fatigue and bloating were less frequent and were mainly reported by patients older than 40.
Conclusion: The commonest presenting features of FAP are alteration of bowel habit and rectal bleeding, but both are found in many other conditions. Patients with these findings need immediate endoscopy to allow prompt diagnosis and prophylactic surgery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does early colectomy increase desmoid risk in familial adenomatous polyposis?Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Oct;5(10):1190-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.06.010. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17916546
-
[Desmoid tumour as indication of familial adenomatous polyposis].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2010;154:A2235. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2010. PMID: 20977806 Dutch.
-
Multicenter experience with upper gastrointestinal polyps in pediatric patients with familial adenomatous polyposis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr;99(4):681-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04115.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15089902
-
Education and management of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Are we making progress? A case report.Rom J Gastroenterol. 2004 Dec;13(4):333-6. Rom J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15624032 Review.
-
[Desmoid tumors in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2002 Jul 20;146(29):1355-9. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2002. PMID: 12162172 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Evaluating causes of death in familial adenomatous polyposis.J Gastrointest Surg. 2010 Dec;14(12):1943-9. doi: 10.1007/s11605-010-1288-6. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010. PMID: 20676788
-
Genetically modified pigs to model human diseases.J Appl Genet. 2014 Feb;55(1):53-64. doi: 10.1007/s13353-013-0182-9. J Appl Genet. 2014. PMID: 24234401 Review.
-
Genetically engineered pigs as models for human disease.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Jan 22;11(1):dmm030783. doi: 10.1242/dmm.030783. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29419487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How harmful is genetic testing for familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) in young children; the parents' experience.Fam Cancer. 2014 Sep;13(3):391-9. doi: 10.1007/s10689-014-9724-5. Fam Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24838933
-
Bloating and functional gastro-intestinal disorders: where are we and where are we going?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 21;20(39):14407-19. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14407. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25339827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bisgaard ML, Fenger K, Bulow S, Niebuhr E, Mohr J. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): frequency, penetrance, and mutation rate. Hum Mutat. 1994;3:121–125. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous