Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation
- PMID: 15740636
- PMCID: PMC1317089
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290271
Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation
Abstract
Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) are evolutionarily conserved zinc finger-containing transcription factors with diverse regulatory functions in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and embryogenesis. KLF4 and KLF5 are two closely related members of the KLF family that have a similar tissue distribution in embryos and adults. However, the two KLFs often exhibit opposite effects on regulation of gene transcription, despite binding to similar, if not identical, cis-acting DNA sequences. In addition, KLF4 and 5 exert contrasting effects on cell proliferation in many instances; while KLF4 is an inhibitor of cell growth, KLF5 stimulates proliferation. Here we review the biological properties and biochemical mechanisms of action of the two KLFs in the context of growth regulation.
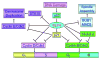
Figures

References
-
- Yang VW. Eukaryotic transcription factors: identification, characterization and functions. J Nutr. 1998;128:2045–51. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Schuh R, Aicher W, Gaul U, et al. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986;47:1025–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

