Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis
- PMID: 15741182
- PMCID: PMC552951
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki200
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis
Abstract
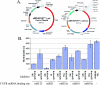
Of the over 200 identified mammalian microRNAs (miRNAs), only a few have known biological activity. To gain a better understanding of the role that miRNAs play in specific cellular pathways, we utilized antisense molecules to inhibit miRNA activity. We used miRNA inhibitors targeting miR-23, 21, 15a, 16 and 19a to test efficacy of antisense molecules in reducing miRNA activity on reporter genes bearing miRNA-binding sites. The miRNA inhibitors de-repressed reporter gene activity when a miRNA-binding site was cloned into its 3'-untranslated region. We employed a library of miRNA inhibitors to screen for miRNA involved in cell growth and apoptosis. In HeLa cells, we found that inhibition of miR-95, 124, 125, 133, 134, 144, 150, 152, 187, 190, 191, 192, 193, 204, 211, 218, 220, 296 and 299 caused a decrease in cell growth and that inhibition of miR-21 and miR-24 had a profound increase in cell growth. On the other hand, inhibition of miR-7, 19a, 23, 24, 134, 140, 150, 192 and 193 down-regulated cell growth, and miR-107, 132, 155, 181, 191, 194, 203, 215 and 301 increased cell growth in lung carcinoma cells, A549. We also identified miRNA that when inhibited increased the level of apoptosis (miR-1d, 7, 148, 204, 210, 216 and 296) and one miRNA that decreased apoptosis (miR-214) in HeLa cells. From these screens, we conclude that miRNA-mediated regulation has a complexity of cellular outcomes and that miRNAs can be mediators of regulation of cell growth and apoptosis pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel D.P. MiRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y., Ahn C., Han J., Choi H., Kim J., Yim J., Lee J., Provost P., Radmark O., Kim S., Kim V.N. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates miRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425:415–419. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G., Zamore P.D. A miRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science. 2002;297:2056–2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

