Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus-protease inhibitor, ritonavir, on basal and catecholamine-stimulated lipolysis
- PMID: 15741249
- PMCID: PMC1350765
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2004-2194
Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus-protease inhibitor, ritonavir, on basal and catecholamine-stimulated lipolysis
Abstract
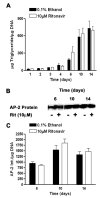
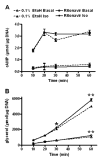
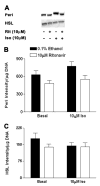
Several of the aspartic acid protease inhibitors used to treat HIV infection increase basal lipolysis in adipocytes, but the cellular mechanisms leading to this augmentation are not well understood. We therefore studied the effects of chronic exposure to the HIV protease inhibitor, ritonavir, on the lipolytic cascade in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes with ritonavir for 14 d (during and after differentiation) enhanced basal, isoproterenol (Iso)-stimulated, and cAMP analog-stimulated lipolysis. Enhancement of lipolysis was observed after Iso at concentrations between 0.1 and 10 mum. Despite a significant decrease in cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE)3B activity and protein levels, there were no changes in Iso-stimulated intracellular cAMP, protein kinase A (PKA) expression, or PKA activity. Ritonavir-augmented lipolysis was also observed under conditions that reversed the effect on PDE3B activity via preincubation with 1 mum (-)-N(6)-(2-phenylisopropyl)adenosine. In ritonavir-treated cells, protein expression of the lipid droplet-protective protein, perilipin, was significantly decreased, whereas there was no change in hormone-sensitive lipase. Activation of ERK1/2 by Iso did not play a role in the augmentation. We conclude that ritonavir decreases PDE3B and perilipin protein expression and affects both basal and catecholamine-stimulated lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes primarily through actions at sites downstream of PKA.
Figures





References
-
- Eron JJ., Jr HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30(Suppl 2):S160–S170. - PubMed
-
- Wlodawer A, Gustchina A. Structural and biochemical studies of retro-viral proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1477:16–34. - PubMed
-
- Rana KZ, Dudley MN. Human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors. Pharmacotherapy. 1999;19:35–59. - PubMed
-
- Wlodawer A, Vondrasek J. Inhibitors of HIV-1 protease: a major success of structure-assisted drug design. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:249–284. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Out-patient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

