Members of the heat-shock protein 70 family promote cancer cell growth by distinct mechanisms
- PMID: 15741319
- PMCID: PMC551577
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.305405
Members of the heat-shock protein 70 family promote cancer cell growth by distinct mechanisms
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Members of the heat-shock protein 70 family promote cancer cell growth by distinct mechanisms.Genes Dev. 2024 Jul 1;38(13-14):692. doi: 10.1101/gad.352065.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39164094 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
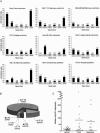
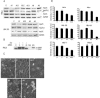
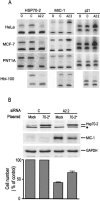
Whereas the stress-inducible heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70) has gained plenty of attention as a putative target for tumor therapy, little is known about the role of other Hsp70 proteins in cancer. Here we present the first thorough analysis of the expression and function of the cytosolic Hsp70 proteins in human cancer cells and identify Hsp70-2, a protein essential for spermatogenesis, as an important regulator of cancer cell growth. Targeted knock-down of the individual family members by RNA interference revealed that both Hsp70 and Hsp70-2 were required for cancer cell growth, whereas the survival of tumorigenic as well as nontumorigenic cells depended on Hsc70. Cancer cells depleted for Hsp70 and Hsp70-2 displayed strikingly different morphologies (detached and round vs. flat senescent-like), cell cycle distributions (G2/M vs. G1 arrest) and gene expression profiles. Only Hsp70-2 depletion induced the expression of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 that was identified as a target of P53 tumor-suppressor protein and a mediator of the G1 arrest and the senescent phenotype. Importantly, concomitant depletion of Hsp70 and Hsp70-2 had a synergistic antiproliferative effect on cancer cells. Thus, highly homologous Hsp70 proteins bring about nonoverlapping functions essential for cell growth and survival.
Figures




References
-
- Albertoni M., Shaw, P.H., Nozaki, M., Godard, S., Tenan, M., Hamou, M.F., Fairlie, D.W., Breit, S.N., Paralkar, V.M., de Tribolet, N., et al. 2002. Anoxia induces macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) in glioblastoma cells independently of p53 and HIF-1. Oncogene 21: 4212-4219. - PubMed
-
- Baek S.J., Kim, K.S., Nixon, J.B., Wilson, L.C., and Eling, T.E. 2001. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors regulate the expression of a TGF-β superfamily member that has proapoptotic and anti-tumorigenic activities. Mol. Pharmacol. 59: 901-908. - PubMed
-
- Bottner M., Suter-Crazzolara, C., Schober, A., and Unsicker, K. 1999. Expression of a novel member of the TGF-β superfamily, growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage-inhibiting cytokine-1 (GDF-15/MIC-1) in adult rat tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 297: 103-110. - PubMed
-
- Buckhaults P., Rago, C., St Croix, B., Romans, K.E., Saha, S., Zhang, L., Vogelstein, B., and Kinzler, K.W. 2001. Secreted and cell surface genes expressed in benign and malignant colorectal tumors. Cancer Res. 61: 6996-7001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
