FGF8 initiates inner ear induction in chick and mouse
- PMID: 15741321
- PMCID: PMC551580
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1273605
FGF8 initiates inner ear induction in chick and mouse
Abstract
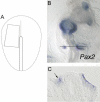
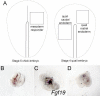
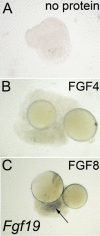
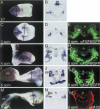
In both chick and mouse, the otic placode, the rudiment of the inner ear, is induced by at least two signals, one from the cephalic paraxial mesoderm and the other from the neural ectoderm. In chick, the mesodermal signal, FGF19, induces neural ectoderm to express additional signals, including WNT8c and FGF3, resulting in induction of the otic placode. In mouse, mesodermal Fgf10 acting redundantly with neural Fgf3 is required for induction of the placode. To determine how the mesodermal inducers of the otic placode are localized, we took advantage of the unique strengths of the two model organisms. We show that endoderm is necessary for otic induction in the chick and that Fgf8, expressed in the chick endoderm subjacent to Fgf19, is both sufficient and necessary for the expression of Fgf19 in the mesoderm. In the mouse, Fgf8 is also expressed in endoderm as well as in other germ layers in the periotic placode region. We show that otic induction fails in embryos null for Fgf3 and hypomorphic for Fgf8 and expression of mesodermal Fgf10 is reduced. Thus, Fgf8 plays a critical upstream role in an FGF signaling cascade required for otic induction in chick and mouse.
Figures


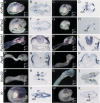
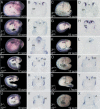
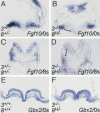
Similar articles
-
Mouse FGF15 is the ortholog of human and chick FGF19, but is not uniquely required for otic induction.Dev Biol. 2004 May 1;269(1):264-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.02.003. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15081372
-
Fgf8 and Fgf3 are required for zebrafish ear placode induction, maintenance and inner ear patterning.Mech Dev. 2002 Nov;119(1):91-108. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(02)00343-x. Mech Dev. 2002. PMID: 12385757
-
FGF signaling regulates otic placode induction and refinement by controlling both ectodermal target genes and hindbrain Wnt8a.Dev Biol. 2010 Apr 15;340(2):595-604. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.02.016. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20171206 Free PMC article.
-
The first steps towards hearing: mechanisms of otic placode induction.Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(6-7):463-72. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072320to. Int J Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17891709 Review.
-
Expression and functions of FGF ligands during early otic development.Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(6-7):473-81. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072334ts. Int J Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17891710 Review.
Cited by
-
Fgf10 is required for specification of non-sensory regions of the cochlear epithelium.Dev Biol. 2015 Apr 1;400(1):59-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25624266 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling during cochlear development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 May;24(5):480-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Mar 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23548730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meis2 Is Required for Inner Ear Formation and Proper Morphogenesis of the Cochlea.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 28;9:679325. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.679325. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34124068 Free PMC article.
-
Making a head: Neural crest and ectodermal placodes in cranial sensory development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 30;138:15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.06.009. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35760729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
sox2 and sox3 cooperate to regulate otic/epibranchial placode induction in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2018 Mar 1;435(1):84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.01.011. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29355522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamska M., Herbrand, H., Adamski, M., Kruger, M., Braun, T., and Bober, E. 2001. FGFs control the patterning of the inner ear but are not able to induce the full ear program. Mech. Dev. 109: 303-313. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez I.S. and Navascues, J. 1990. Shaping, invagination, and closure of the chick embryo otic vesicle: Scanning electron microscopic and quantitative study. Anat. Rec. 228: 315-326. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez Y., Alonso, M.T., Vendrell, V., Zelarayan, L.C., Chamero, P., Theil, T., Bosl, M.R., Kato, S., Maconochie, M., Riethmacher, D., et al. 2003. Requirements for FGF3 and FGF10 during inner ear formation. Development 130: 6329-6338. - PubMed
-
- Anniko M. and Wikstrom, S.O. 1984. Pattern formation of the otic placode and morphogenesis of the otocyst. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 5: 373-381. - PubMed
-
- Baker C.V. and Bronner-Fraser, M. 2001. Vertebrate cranial placodes I. Embryonic induction. Dev. Biol. 232: 1-61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
